
Anatomy and Physiology Sensory Perception
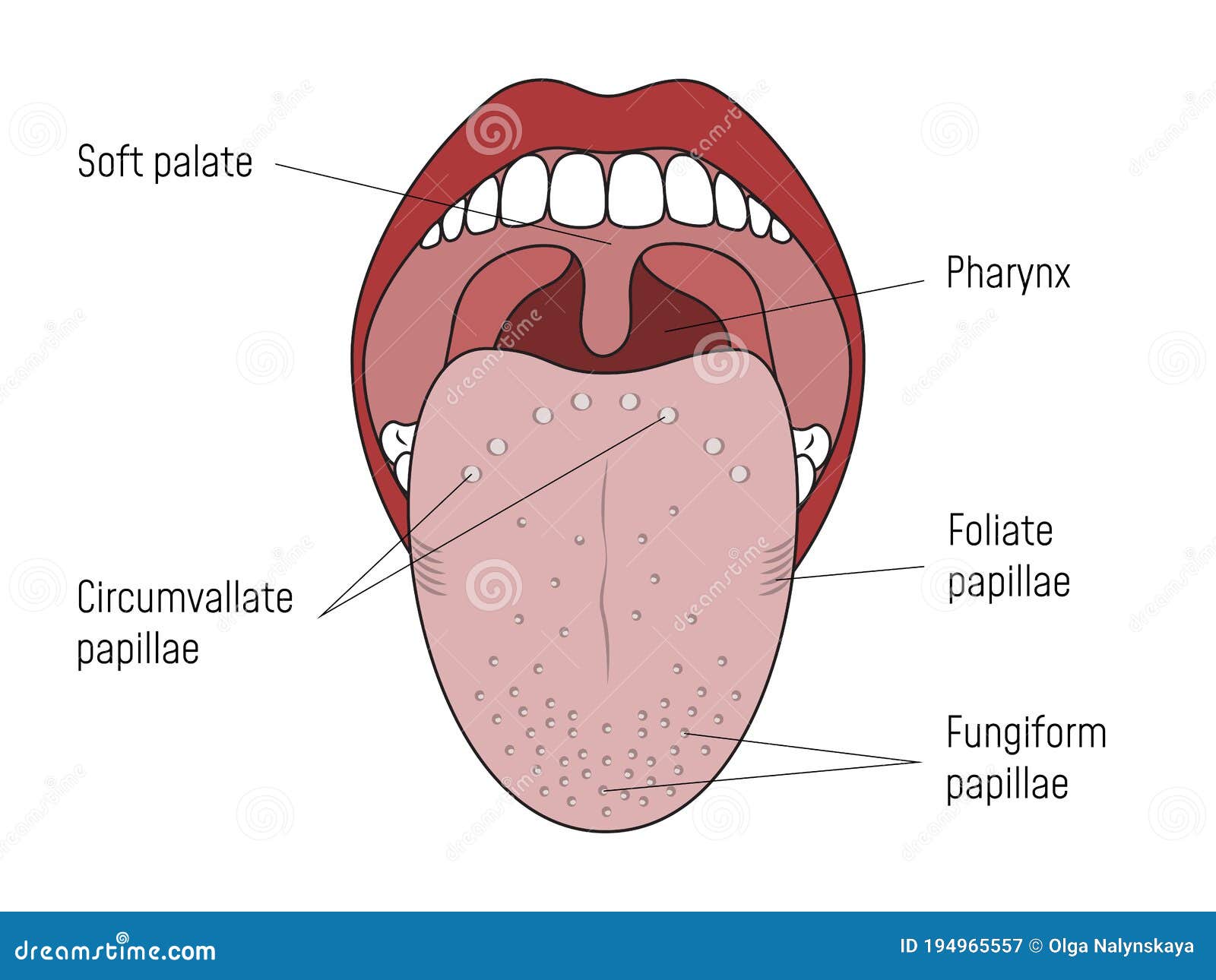
3 min read Image Source © 2014 WebMD, LLC. All rights reserved. The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth. The tongue is covered with moist, pink tissue called mucosa. Tiny bumps called.
Lingual Gustatory Papillae and Taste Buds Human Mouth Stock Vector Illustration of biology
Read about the human tongue and view a tongue diagram. Learn about the parts of the tongue, which includes taste buds, and learn about the tongue's function. Updated: 09/13/2022 What is.
Anatomical structure tongue taste buds on Vector Image
Anatomical Structure of Human Tongue (With Diagram) | Biology Article Shared by ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the anatomical structure of human tongue with the help of suitable diagrams. Tongue (Fig. 9.5) is made up of three elements; epithelium, muscles and glands. The epithelium is stratified and non-cornified.
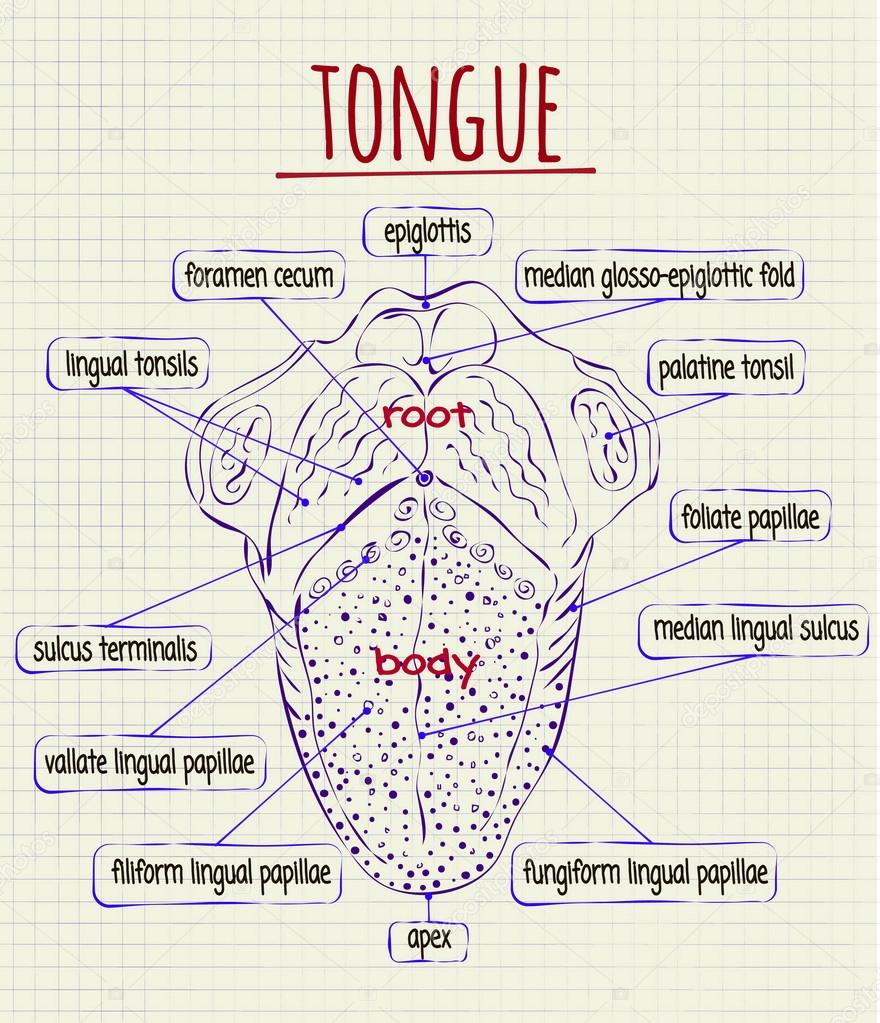
Diagram of the anatomy of human tongue Stock Vector Image by ©Silbervogel 83471906
Anatomy Where is the tongue located? Your tongue runs from your hyoid bone (located in the middle of your neck) to the floor of your mouth. Advertisement What is the tongue made of? Your tongue is mostly made of muscles.

Anatomy Of Tongue ANATOMY
The first part of the digestive system that contains the structures necessary for mastication and speech; teeth, tongue and salivary glands. Tongue. A muscular organ in the oral cavity that enables taste sensation, chewing, swallowing and speaking. Muscles of the tongue. Intrinsic: Superior longitudinal, inferior longitudinal, transverse and.
The Tongue
Figure 1. A Sagittal view of the external muscles of the tongue, B sagittal and C anterior cross-section view of the internal muscles of the tongue. Figure 2. Sagittal view of the tongue in the oral cavity. B Superior view of the tongue. Figure 3. Inferior view of the tongue. Figure 4. Sensory innervation of the tongue. Figure 5.

The Tongue Diagram Quizlet
The taste buds are bulb-shaped structures responsible for taste perception, located within the lingual papillae and in the surface mucosa of the soft palate, oropharynx, epiglottis, and upper esophagus. It is the only extrinsic muscle of the tongue that is not innervated by the hypoglossal nerve but by the vagus nerve (CN X). Contraction of the.

Human Tongue Anatomy Human tongue, Tongue health, Anatomy
Human body Digestive System Tongue Tongue The tongue is unique in that it is the only muscle that isn't connected to bone at both ends. It is connected on one end to the hyoid bone, which is.
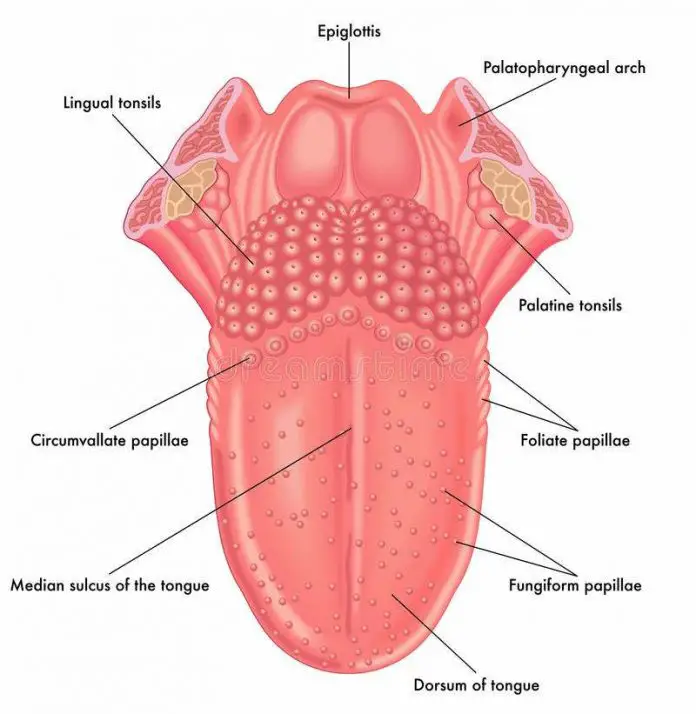
Diagram of tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ of the oral cavity and is an accessory digestive organ in the digestive system. It has many functions of which the most important are mastication, taste, swallowing, speech, and clearing the oral cavity.
How to Draw Diagram Of Tongue YouTube
Anatomy Function Associated Conditions Tests Taste buds are a small organ located primarily on the tongue. The adult human tongue contains between 2,000 and 8,000 taste buds, each of which are made up of 50 to 150 taste receptor cells. Taste receptor cells are responsible for reporting the sense of taste to the brain .

Dorsal Surface Of Tongue , Png Download Tongue Diagram Simple, Transparent Png , Transparent
It is made up of four pairs of muscles: 1 Intrinsic (entirely within the tongue): superior longitudinal, inferior longitudinal, vertical, and transverse muscles. Their role is to change the shape of the tongue, having a role in facilitating speech, eating, and swallowing.

Tongue Anatomy Diagram
The human tongue is a muscular organ that is covered by a thin mucous membrane. It lies partly in the mouth cavity and partly in the oropharynx. It is highly mobile and can be shifted into a number of different positions and also assume various shapes.

Anatomy Human Tongue Parts Illustration Depicting Anatomy Taste Tongue Its Stock Vector by
The tongue also determines whether a vowel is tense or lax. Both the "ee" and "ah" I discussed are tense—the schwa (ə), as in the first syllable of "maroon," is a good example of a lax vowel. You can read more about the anatomy and physiology of speech sounds here. For now, let's move on to the tongue's role in swallowing food.
6b3 Senses HumanBio
Overview. The tongue is a mass of muscle that is almost completely covered by a mucous membrane. It occupies most of the oral cavity and oropharynx. It is known for its role in taste, but it also assists with mastication (chewing), deglutition (swallowing), articulation (speech), and oral cleansing. Five cranial nerves contribute to the complex.
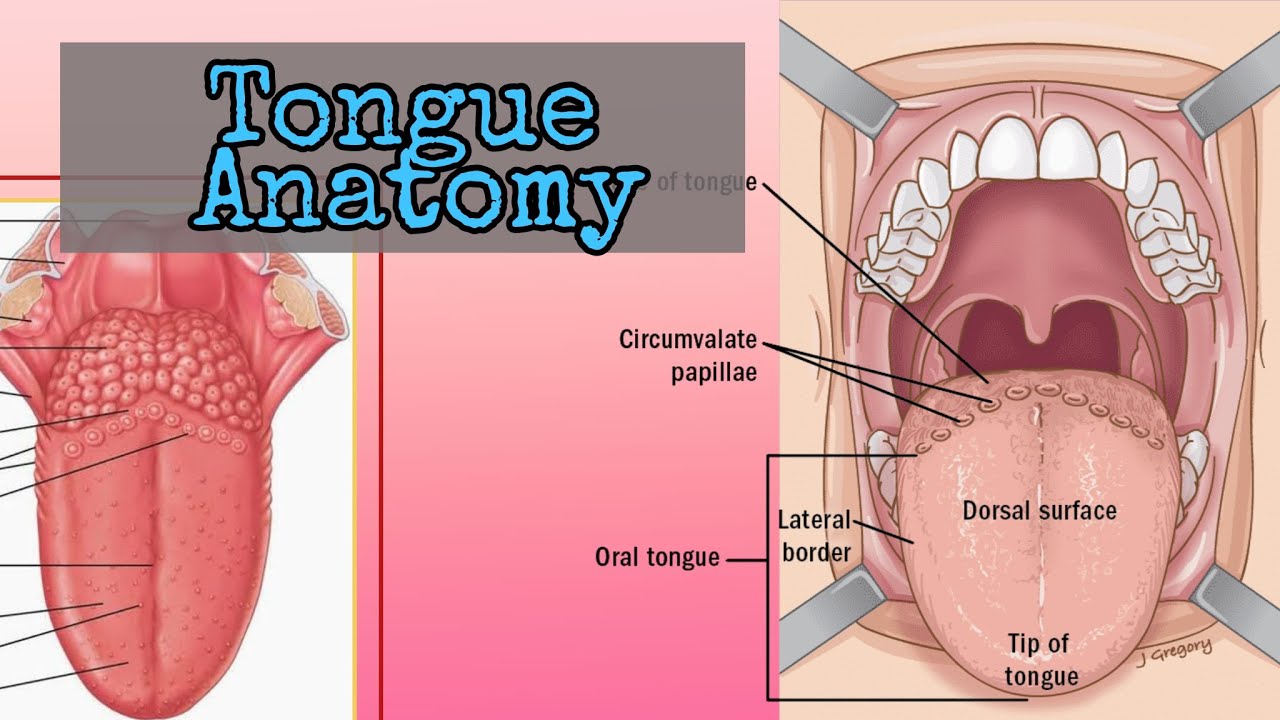
Tongue Surface Anatomy of the Tongue Head and Neck Human Anatomy YouTube
Well-labelled Diagram of Human Tongue Tongue Structure The human tongue can be distinguished into three segments: the base, body, tip, or apex. The apex is present immediately behind the incisor teeth and is considered a mobile aspect of the tongue. It is followed by the body, which has rough superior and smooth inferior surfaces.
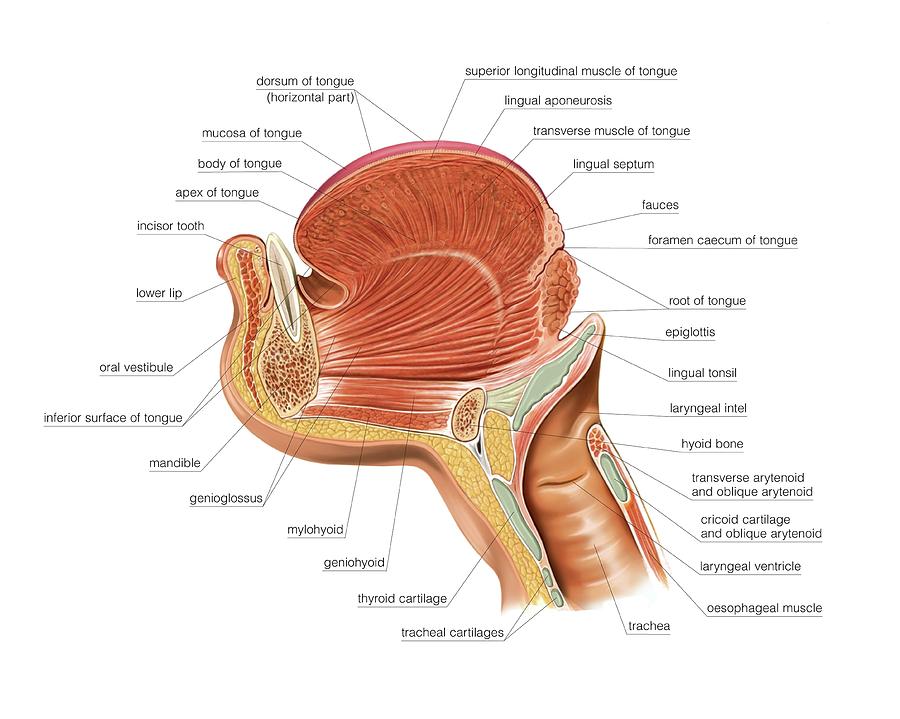
Tongue Anatomy Diagram Anatomical Charts & Posters
The tongue is a mass of muscles covered by a mucous membrane that is important for taste sensation. Beyond its obvious role in eating—manipulating food into a bolus that can be safely passed into the throat with swallowing—it also has a vital contribution to speech. It may even affect breathing, especially in sleep. Eating