
What Happens at The Synapse?
Where two neurons meet there is a small gap called a synapse close synapse A tiny gap at the junction between two nerve cells, which nerve signals must cross..The plasma membranes of each neuron.

Synapses
Mechanism of Synaptic Transmission 3. Properties. Definition of Synapse: Synapse can be defined as functional junction between parts of two different neurons. There is no anatomical continuity between two neurons involved in the formation of synapse.
What Is A Synapse? What Is A Neurotransmitter? How Do They Work?
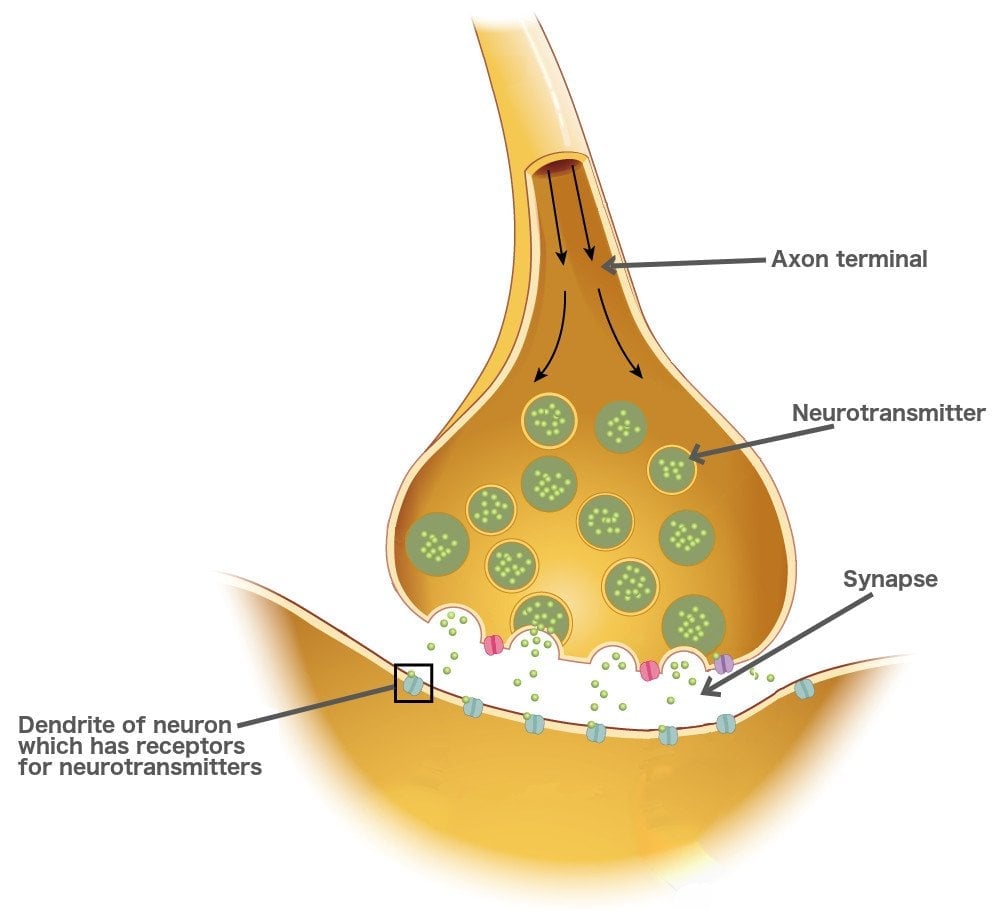
In psychology, a synapse is the junction between two neurons where information is transmitted from one neuron to another. It consists of the axon terminal of the sending neuron, the synaptic cleft (a small gap), and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron.
Synapses Definition, Types and Structure , Anatomy QA
Nervous system introduction © 2024 Khan Academy Terms of use Privacy Policy Cookie Notice Synapse structure Google Classroom About Transcript This video discusses synapses, where neurons communicate with target cells. It differentiates between two types of synapses: chemical and electrical.

Neurotransmitters and receptors
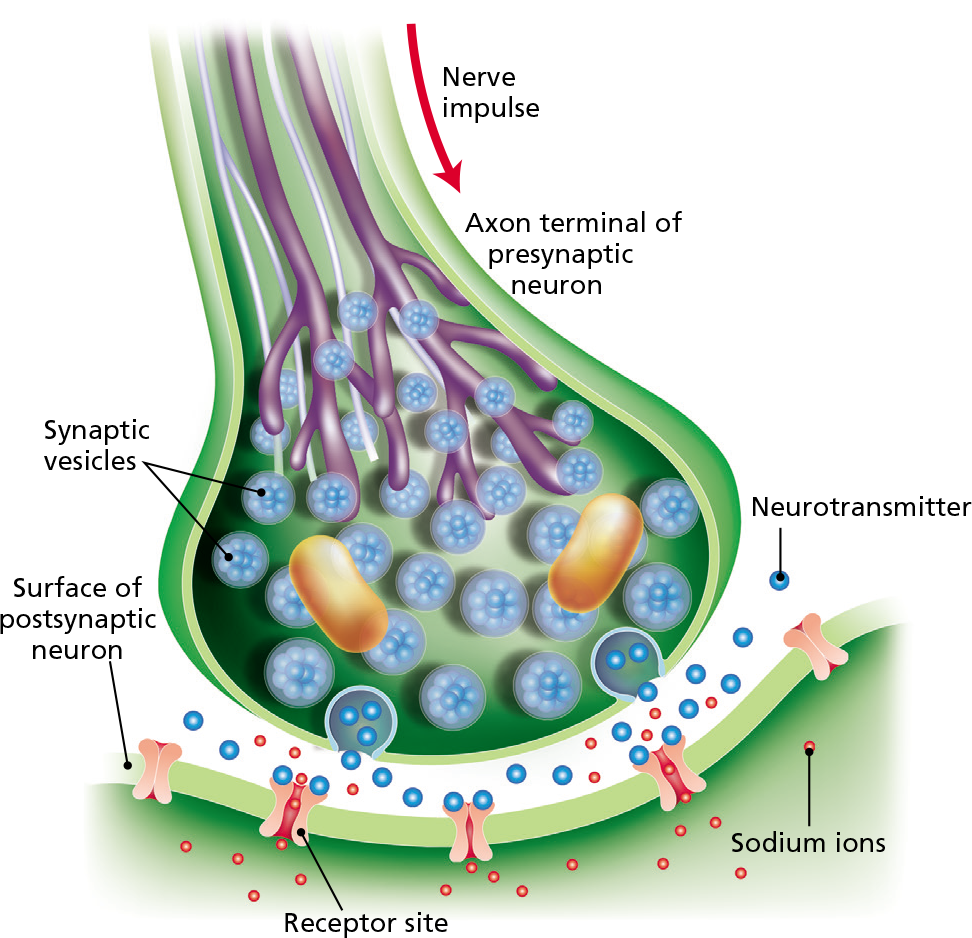
At the synapse, the firing of an action potential in one neuron—the presynaptic, or sending, neuron—causes the transmission of a signal to another neuron—the postsynaptic, or receiving, neuron—making the postsynaptic neuron either more or less likely to fire its own action potential.
Neurotransmission
Synapse diagram Each neuron forms about 2,000 synapses. There are about 10 11 neurons in the CNS. The synapses are of different types and can be classified on the following bases. Parts of neurons involved in the synapse Axodendritic synapse- The axon of the presynaptic neuron connects to the dendrite of the postsynaptic neuron.

Chemical and Electrical Synapses Biology for Majors II
The peripheral nervous system ( PNS ), which consists of the neurons and parts of neurons found outside of the CNS, includes sensory neurons and motor neurons. Sensory neurons bring signals into the CNS, and motor neurons carry signals out of the CNS. _Image modified from " Nervous system diagram ," by Medium69 ( CC BY-SA 4.0 )._
Microglia Maintenance of Neuron Synapses
¡Precios increíbles y alta calidad aquí en Temu. Envío gratuito en todos los pedidos. ¡Solo hoy, disfruta de todas las categorías hasta un 90% de descuento en tu compra.
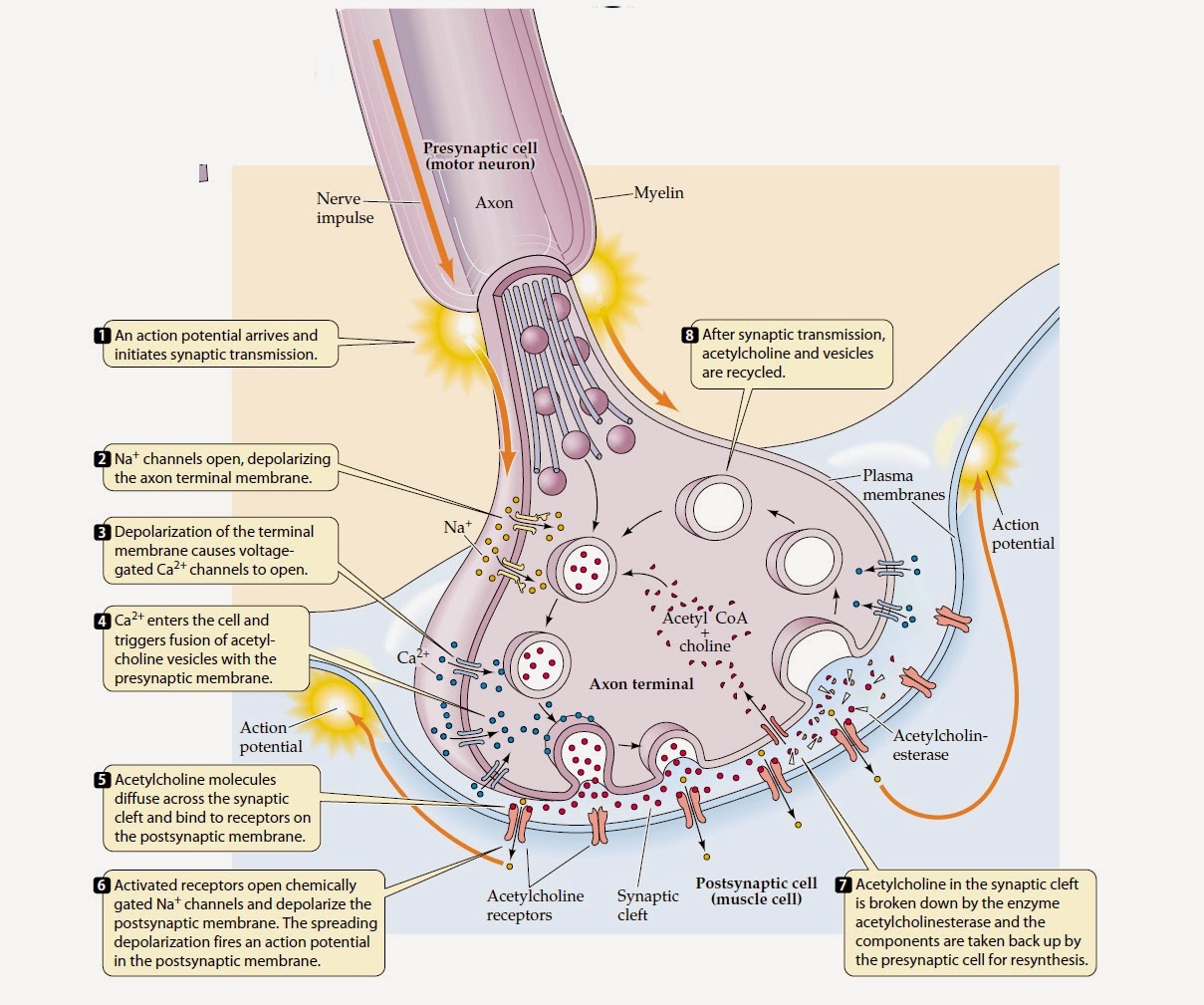
Biology learnspot The Synapse and mechanism of synaptic transmission.
Types Synapses are fundamentally classified into two different types based on how the neurons function to communicate: 1) chemical synapse and 2) electrical synapse. 1) Chemical Synapse Found in vertebrates, it works using neurotransmitters that establish the virtual connection between the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons.

Anatomy synapse cells transmission signal Vector Image
Octopart Is The Preferred Search Engine for Electronic Parts. Search Across Hundreds of Distributors to Compare Prices, Inventory and Save!

Neuronal Synapses Synaptic Transmission in the Nervous System The Nervous System Medical
synapse, the site of transmission of electric nerve impulses between two nerve cells (neurons) or between a neuron and a gland or muscle cell (effector). A synaptic connection between a neuron and a muscle cell is called a neuromuscular junction.

Synapses Anatomy and Physiology I
(A) Electron micrograph of a human synapse with two synaptic junctions to illustrate the canonical features of all synapses: An intercellular junction in which a presynaptic varicosity that is filled with synaptic vesicles contacts a postsynaptic dendrite that contains multiple trafficking organelles as well as ribosomes (image courtesy of Dr. C.

2 A schematic representation of synapse. Download Scientific Diagram
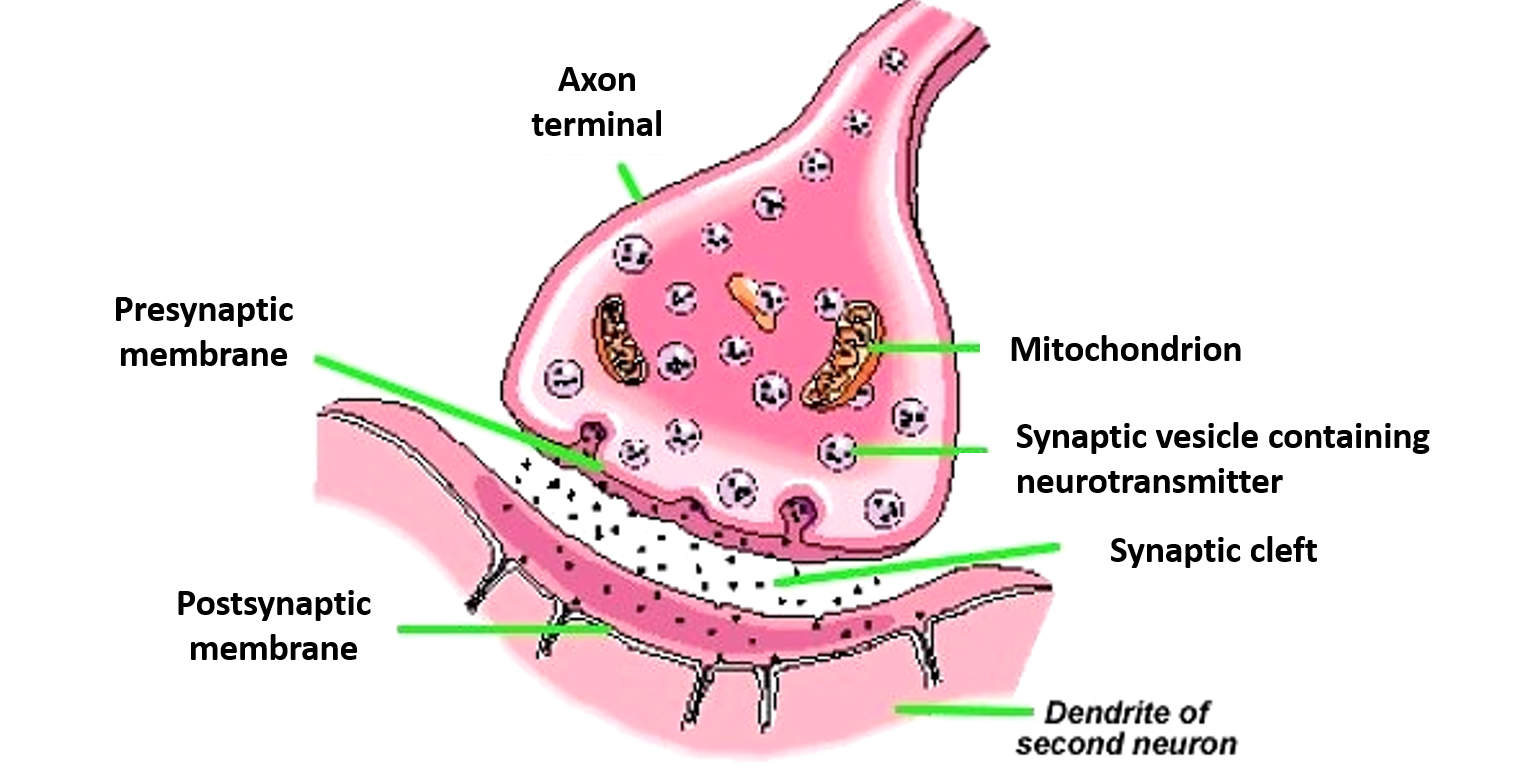
Diagram of a synapse, showing neurotransmitters stored in synaptic vesicles inside the axon terminal. In response to an action potential, the vesicles fuse with the presynaptic membrane and release neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft. Image modified from " The synapse ," by OpenStax College, Anatomy & Physiology ( CC BY 3.0 ).
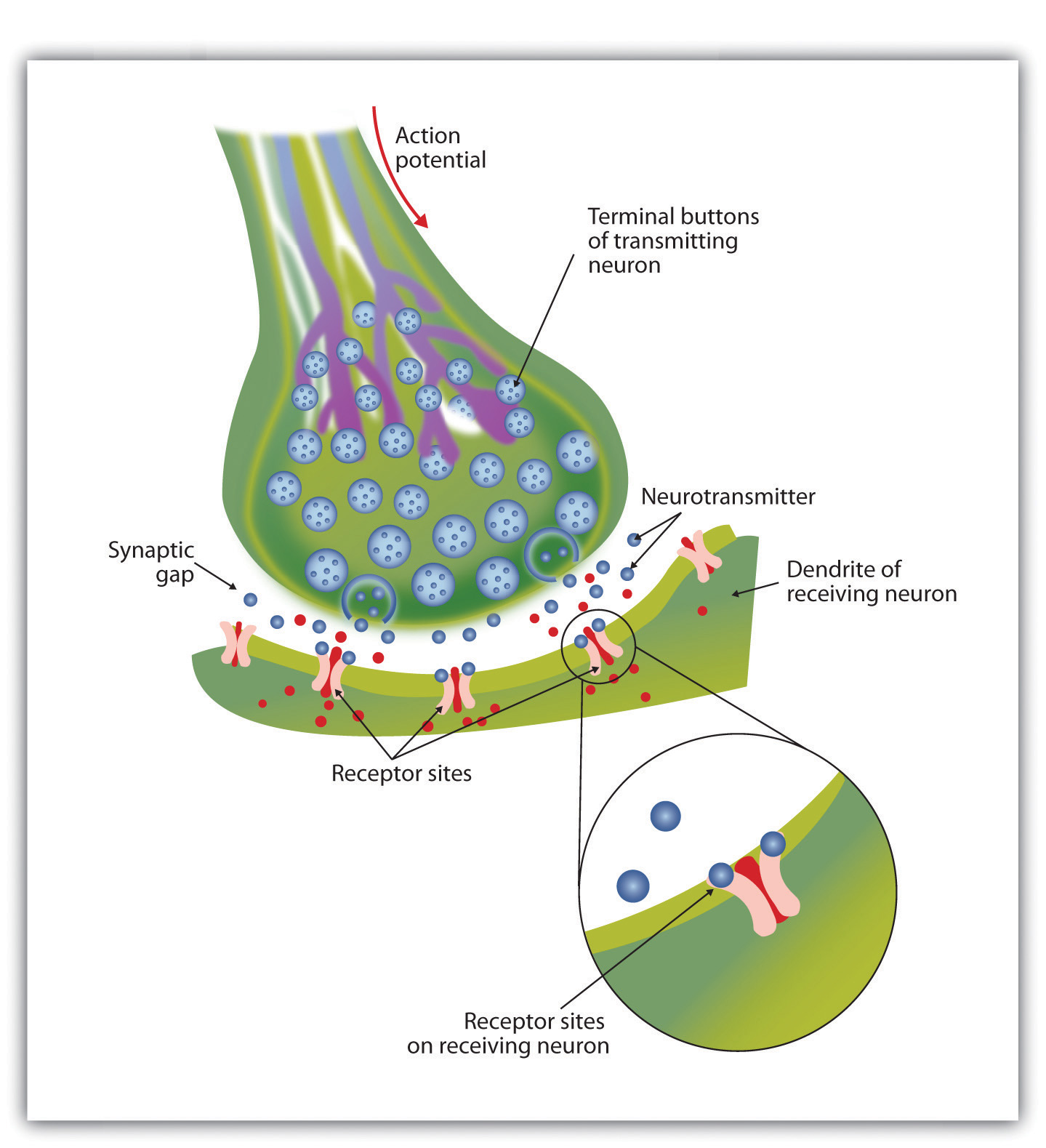
The Neuron Is the Building Block of the Nervous System
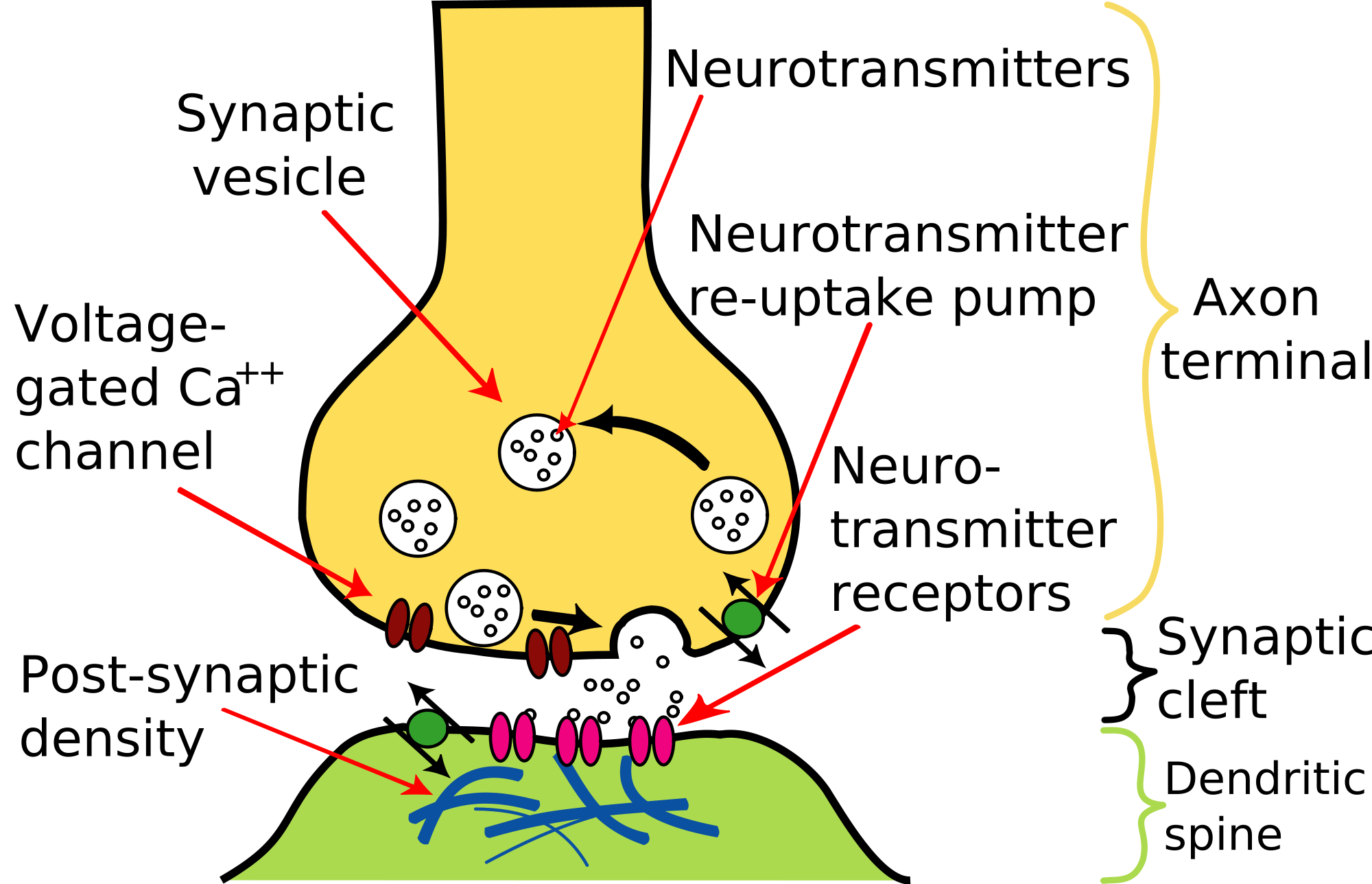
Fig 1 - Diagram showing the basic model of neurotransmission. (A) Presynaptic neuron. (B) Postsynaptic neuron. (1) Mitochondria. (2) Synaptic vesicles containing neurotransmitters. (3) Autoreceptor. (4) Synaptic cleft. (5) Neurotransmitter receptor. (6) Calcium channel. (7) Fused vesicle releasing neurotransmitter.

representative synapse Pearson education, Nerve cell, Cell diagram
Resources. For the nervous system to function, neurons must be able to communicate with each other, and they do this through structures called synapses. At the synapse, the terminal of a presynaptic cell comes into close contact with the cell membrane of a postsynaptic neuron. Figure 8.1. The terminal of a presynaptic neuron comes into close.
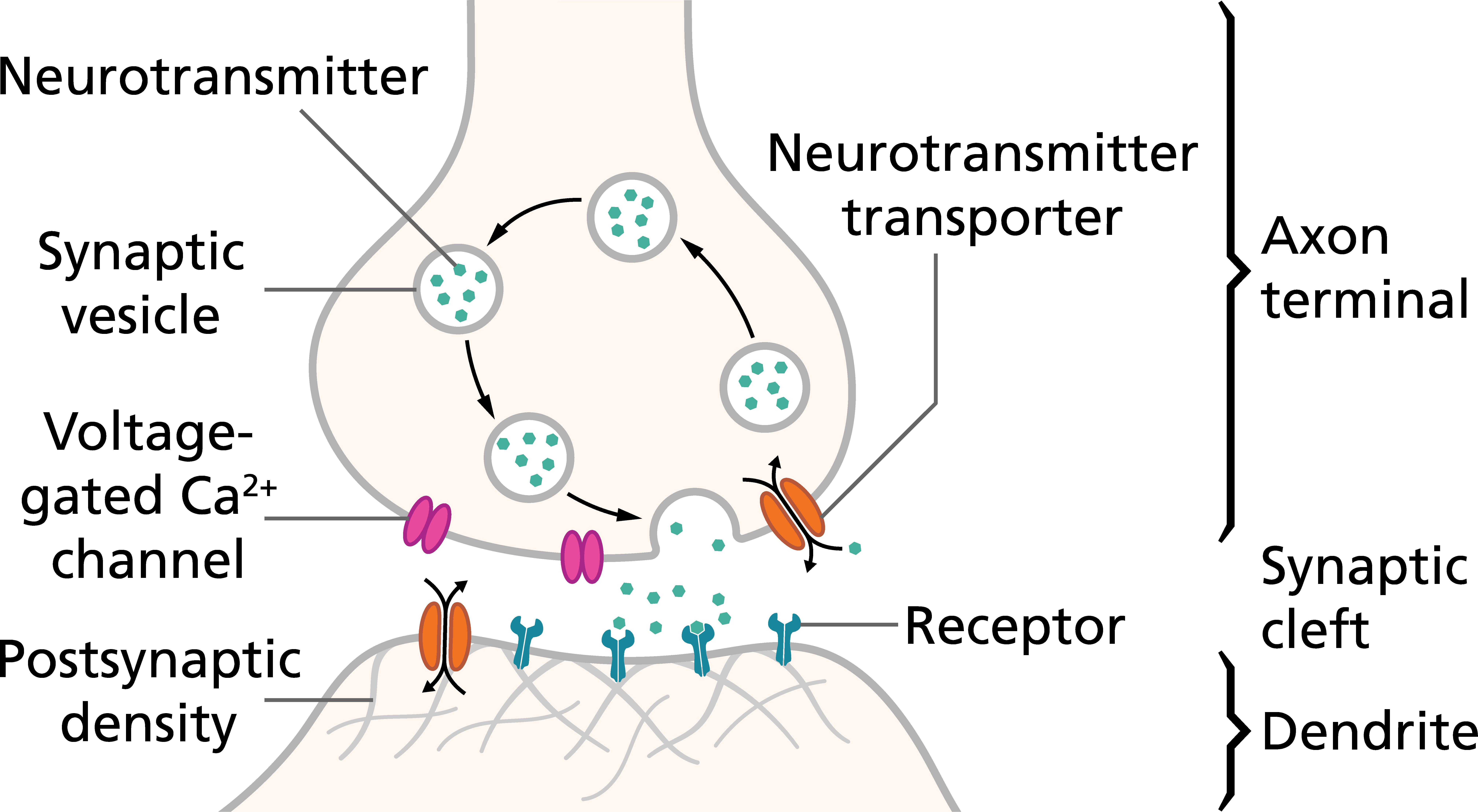
Pitt Medical Neuroscience Synaptic Transmission
The general structure of a chemical synapse is shown schematically in Figure 5.1B. The space between the pre- and postsynaptic neurons is substantially greater at chemical synapses than at electrical synapses and is called the synaptic cleft. However, the key feature of all chemical synapses is the presence of small, membrane-bounded organelles called synaptic vesicles within the presynaptic.