
Dog neck anatomy
The Anatomy of the Canine Digestive System (An Overview) A muscular tube that carries ingesta from the laryngopharynx to the stomach. The esophagus courses through the neck, thorax, and into the abdomen. The esophagus can therefore be referred to as having cervical, thoracic, and abdominal portions. The stomach is a dilation of the alimentary.

Anatomy Of Back Organs / Anatomy Male Organs in Loop Stock Footage
Updated: 10-08-2021 From The Book: Dog Grooming For Dummies Dog Grooming For Dummies Explore Book Buy On Amazon Some canine anatomical names may be familiar to you — dogs have elbows and ears and eyes — but other names may be downright foreign. Many anatomical terms used to describe parts of a dog are similar to the ones used for horses.

Anatomy of dog with inside organ structure examination vector
Anatomic Planes. The main planes of motion for dogs are as follows (see Figure 5-1): • The sagittal plane divides the dog into right and left portions. If this plane were in the midline of the body, this is the median plane or median sagittal plane. • The dorsal plane divides the dog into ventral and dorsal portions.
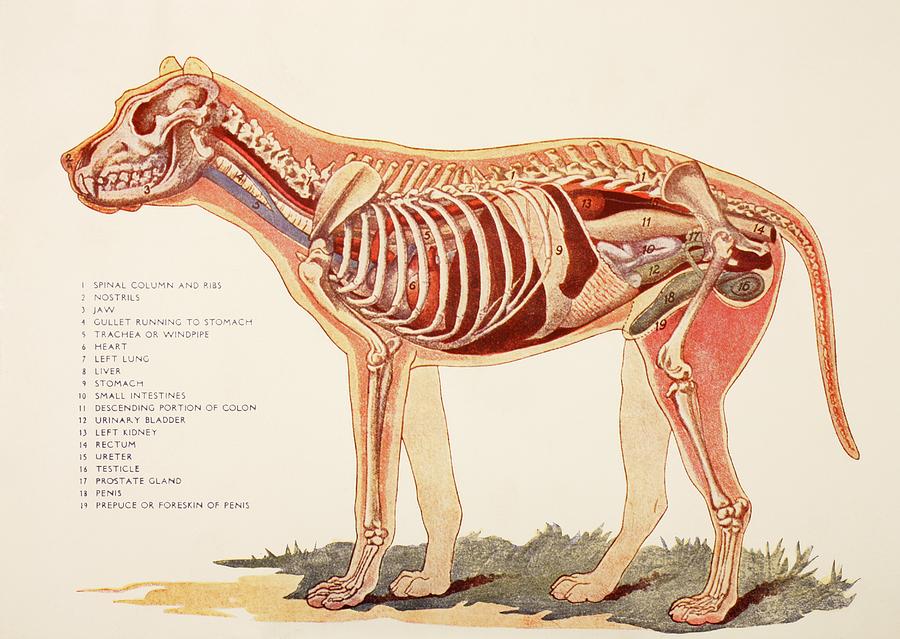
Internal Organs Of A Male Dog. From Photograph by Ken Welsh Fine Art
Lung: respiratory organ. Trachea: tube that carries air to the lungs. Esophagus: last part of the digestive tract. Larynx: part of a dog's throat that contains the vocal cords. Photo : EN : Maltese dog FR : Bichon maltais ES : Bichón maltés Maltese can be very energetic, despite this they still do well for apartment dwellers.
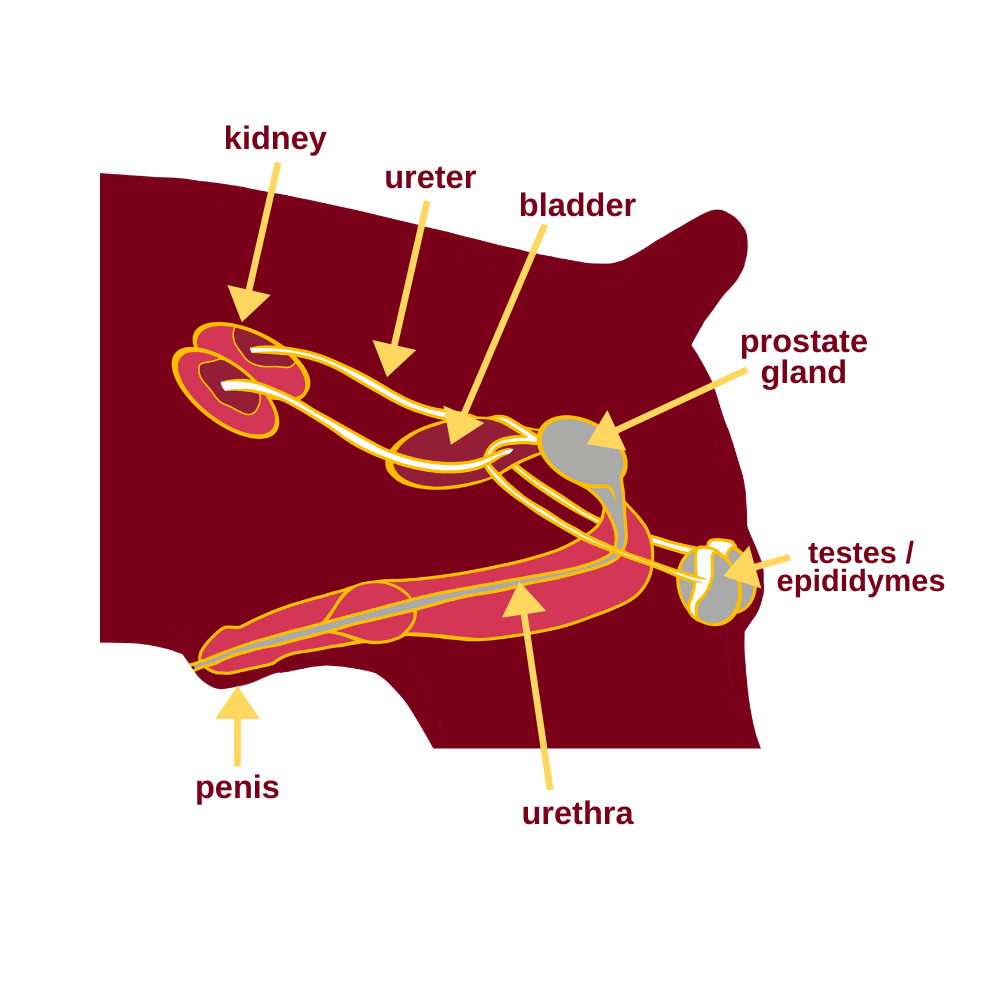
Reproduction Control Veterinary Preventive Medicine
Heart. A dogs heart beats between 70 and 120 times per minute, compared to a humans 70 - 80 beats per minute. Dogs take between 10 and 30 breathes every minute. Dogs have a visual range of 250 degrees compared to the human range of 180 degrees. A dogs temperature is between 100.2 and 102.8 degrees Fahrenheit.
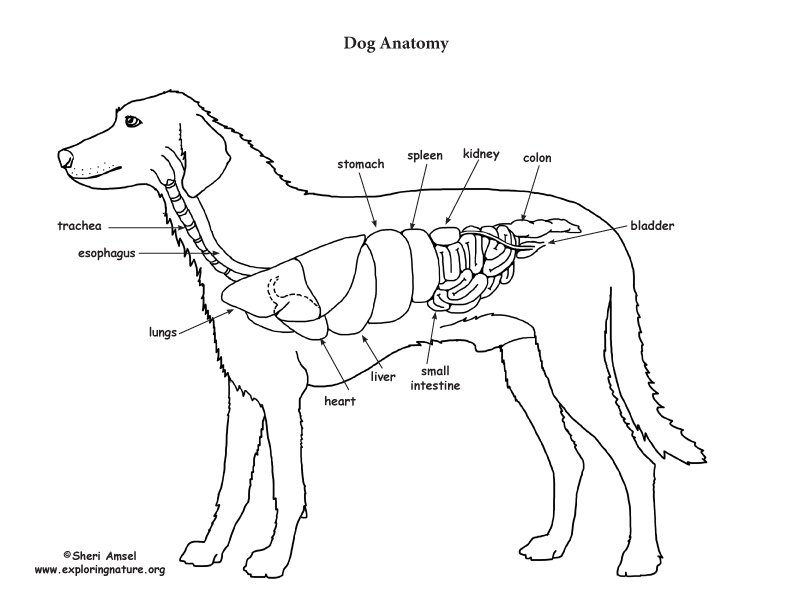
Dog Anatomy (Thoracic and Abdominal Organs)
What are the key body parts for a female dog? Key body parts for a female dog include the head, ears, eyes, nose, mouth, legs, paws, and tail, just like in a male dog. The primary difference between the two lies in the reproductive organs, with female dogs having ovaries, uterus, and a vulva instead of the testicles and penis found in male dogs.
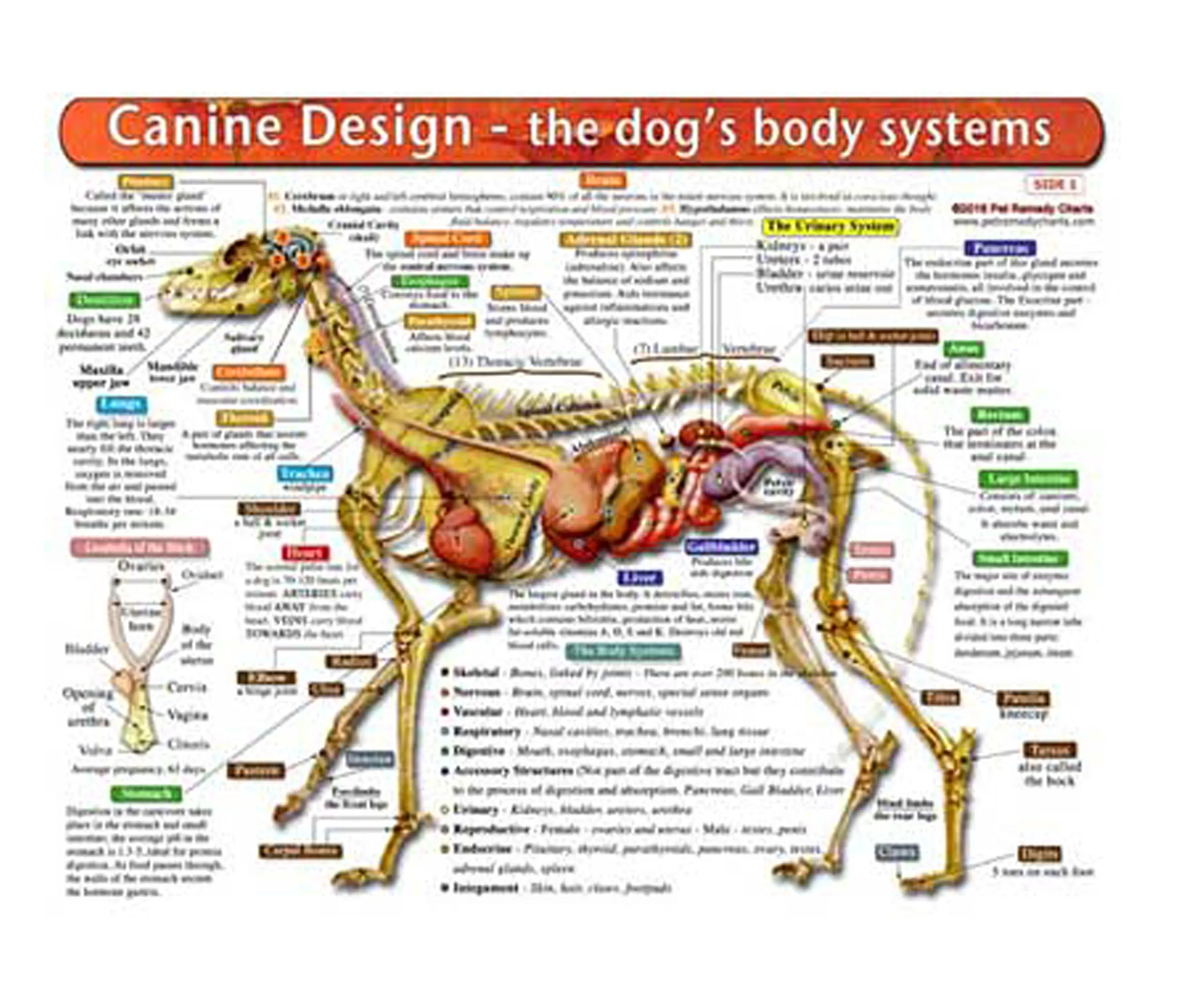
Buy The Dogs Body Systems A DoubleSided, UV Protected, Laminated Dog
Anatomy of a Dog Dog Skeleton Anatomy Dog Muscle Anatomy Female vs Male Dog Anatomy Summary Anatomy of a Dog Dog anatomy details the various structures of canines (e.g. muscle, organ and skeletal anatomy). The detailing of these structures changes based on dog breed due to the huge variation of size in dog breeds.
The 6 Best Probiotics For Dogs Dogs Naturally Magazine
Common anatomical terminology Here are some common veterinary terms and their meanings: Pet senses Pets communicate in a very different way than people do. They have the same basic senses like sight, hearing, smell, touch, and taste, but they use them differently to communicate with the world.

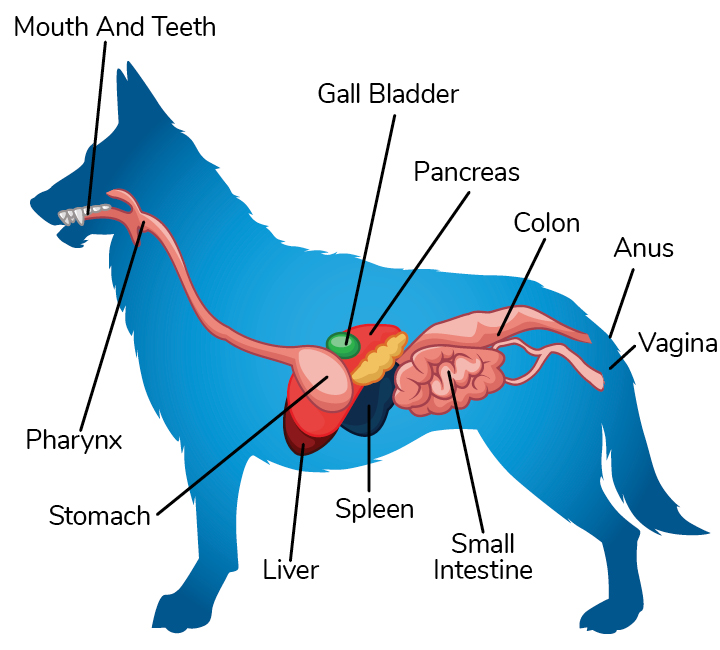
The process of a dog’s digestive system
The dog abdomen anatomy consists of boundaries of the abdominal cavity with its organs and associated structures. This article might help you with the details of anatomical facts of the abdomen, both male and female. First, I will try to show you the exact boundary of the dog's abdomen so that you may also identify it from the live dog.

Pin on Fun Pet Pictures
One of the most important parts of a dog's anatomy is their skeleton. A dog's skeleton is made up of many different bones, which provide structure and support for their body. Dogs have over 300 bones in their body, which is more than humans who have around 206 bones. Their skeleton includes their skull, spine, ribcage and limbs.

Lightbox Detoxapet Detoxapet Dog anatomy, Naturopathic medicine
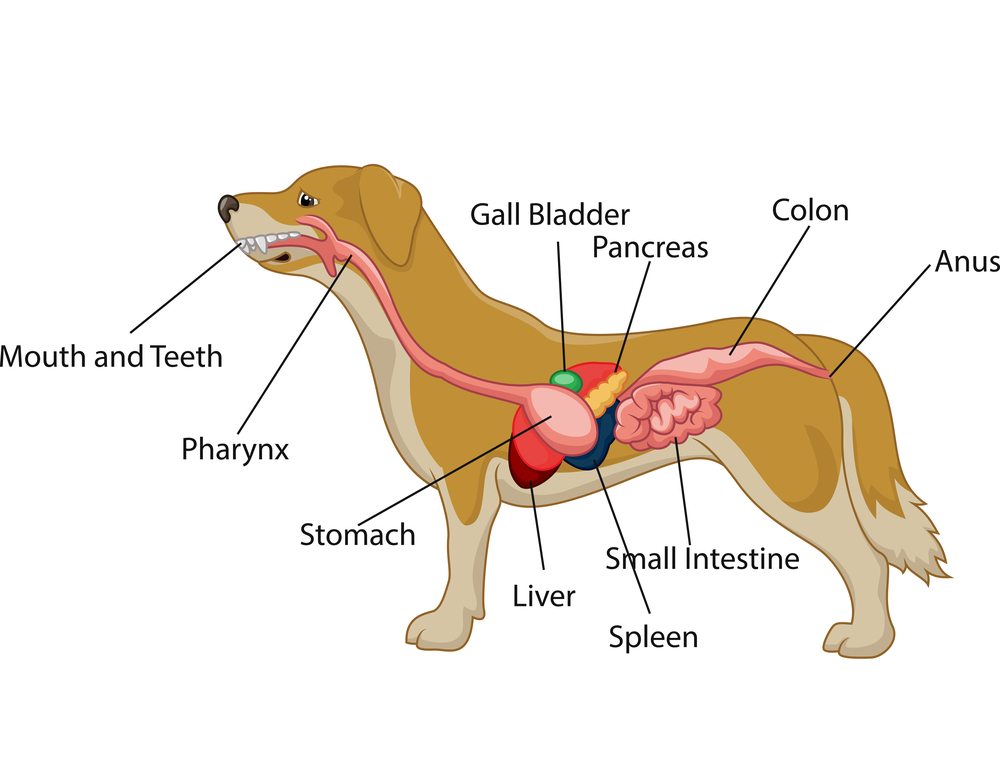
Animal Anatomy (Veterinary Diagrams) Dog Anatomy (Thoracic and Abdominal Organs) High Resolution PDF for Printing. Click Here. Link to More Information About This Animal.. Amsel, Sheri. "Dog Anatomy (Thoracic and Abdominal Organs)" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. January 4, 2024

What To Do For a Dog With Kennel Cough Fidose of Reality
On the left side view of a dog's internal organs, you can see the lungs, heart, liver, stomach, spleen, kidney, intestines, bladder, and the rectum in that order from front to back. You can also view the spinal column and the brain. Laurie O'Keefe Dog Anatomy Organs Right Side
Dog Digestive Process and what the stages are and how it works
A Visual Guide to Understanding Dog Anatomy With Labeled Diagrams Dog anatomy is not very difficult to understand if a labeled diagram is present to provide a graphic illustration of the same. That is exactly what you will find in this DogAppy article.
Dog Anatomy (Thoracic and Abdominal Organs)
This module of vet-Anatomy is a basic atlas of normal imaging anatomy of the dog on radiographs. 51 sampled x-ray images of healthy dogs performed by Susanne AEB Borofka (PhD - dipl. ECVDI, Utrecht, Netherland) were categorized topographically into seven chapters (head, vertebral column, thoracic limb, pelvic limb, larynx/pharynx, thorax and abd.

Dog Internal Anatomy Poster Dog anatomy, Anatomy, Vet medicine
The dog's stomach is a sac-like structure designed to store large volumes of food and continue the digestive process. The esophagus carries food to the stomach, where it enters via a valve-like structure called the cardiac sphincter. On the interior surface of the stomach is a series of folds called gastric folds.

Внутренние органы собаки. Вид справа Dog Internal Organs, Anatomy
Canine anatomy As we explain above, canine anatomy is far ranging due to the diversity of existing breeds. These different breeds not only differ from each other in size, but in the shape of many body parts. Perhaps the most significant is head shape. There are three main different types of head formation in dogs: