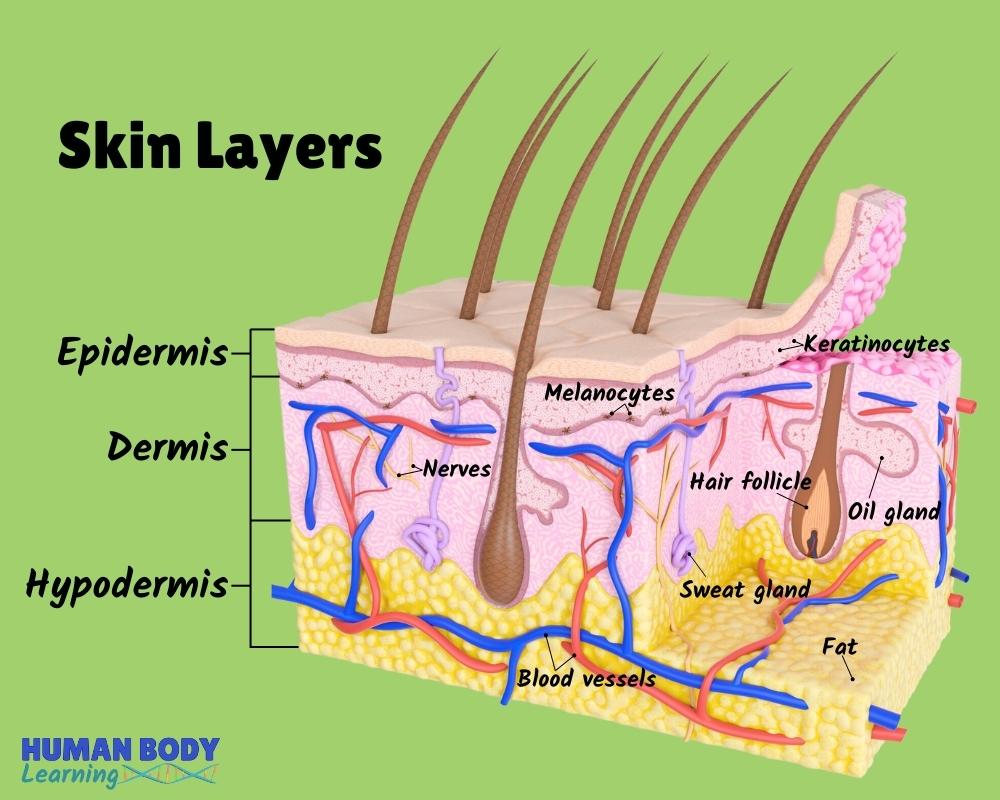
Skin Layers Anatomy Diagram for Kids
katleho Seisa / Getty Images Table of Contents The Epidermis The Dermis Hypodermis The number of skin layers that exists depends on how you count them. You have three main layers of skin—the epidermis , dermis, and hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue). Within these layers are additional layers.

Human skin diagram Subcutaneous tissue, Skin structure, Epidermis
The skin is made up of 3 layers: Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous fat layer (hypodermis) Each layer has certain functions. Epidermis The epidermis is the thin outer layer of the skin. It consists of 2 primary types of cells: Keratinocytes. Keratinocytes comprise about 90% of the epidermis and are responsible for its structure and barrier functions.
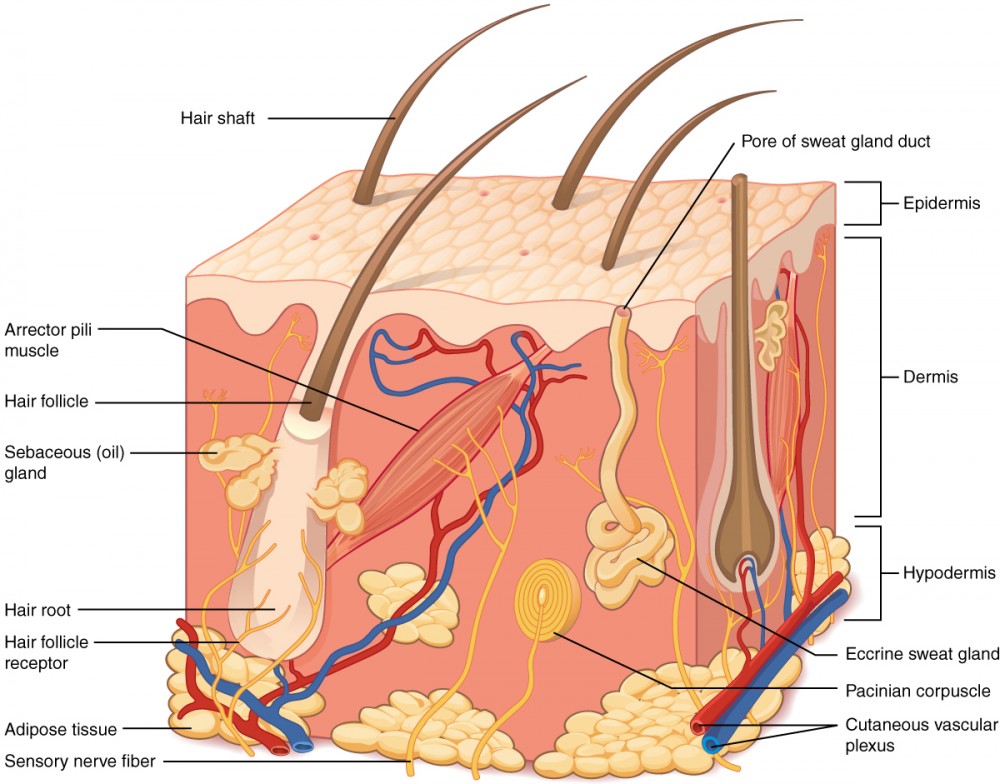
Layers of the Skin Anatomy and Physiology I
Hair, skin and nails Wound healing Osmosis High-Yield Notes This Osmosis High-Yield Note provides an overview of Skin Structures essentials. All Osmosis Notes are clearly laid-out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently. Find more information about Skin Structures:
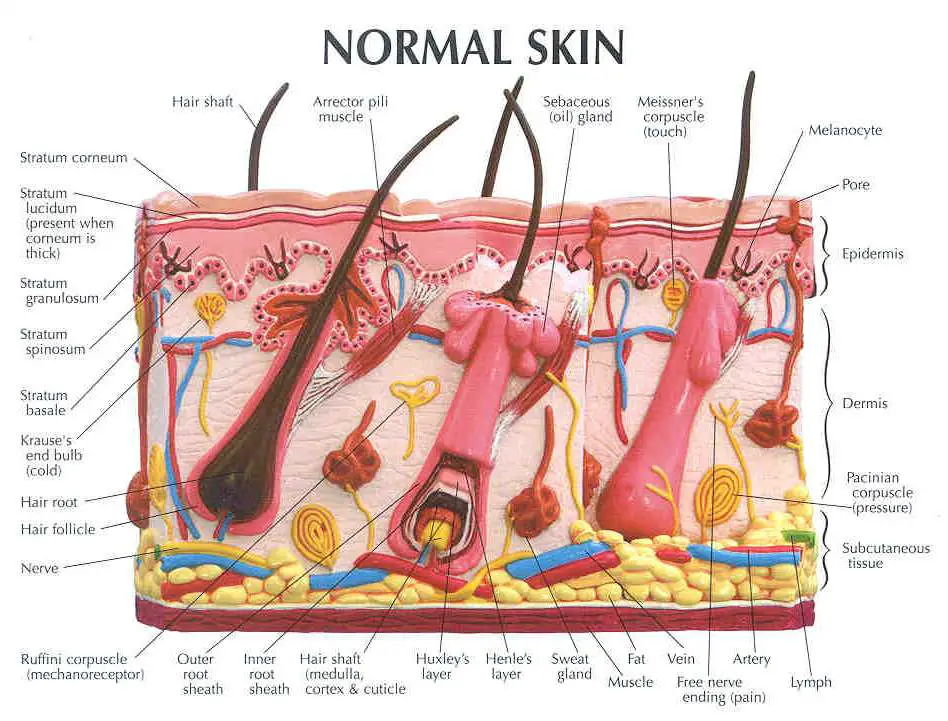
Skin diagram labeled
'Skin Diagram || How to draw and label the parts of skin' is demonstrated in this video tutorial step by step.The sense of touch had received supreme importa.

Some curiosities about the skin Periérgeia
Thin Skin versus Thick Skin. These slides show cross-sections of the epidermis and dermis of (a) thin and (b) thick skin. Note the significant difference in the thickness of the epithelial layer of the thick skin. From top, LM × 40, LM × 40. (Micrographs provided by the Regents of University of Michigan Medical School © 2012)

The Anatomy Of Skin Layers Tissues
This article will discuss the anatomy of the skin, including its structure, function, embryology, blood, lymphatic, and nerve supply, surgical, and clinical significance. [1] [2]
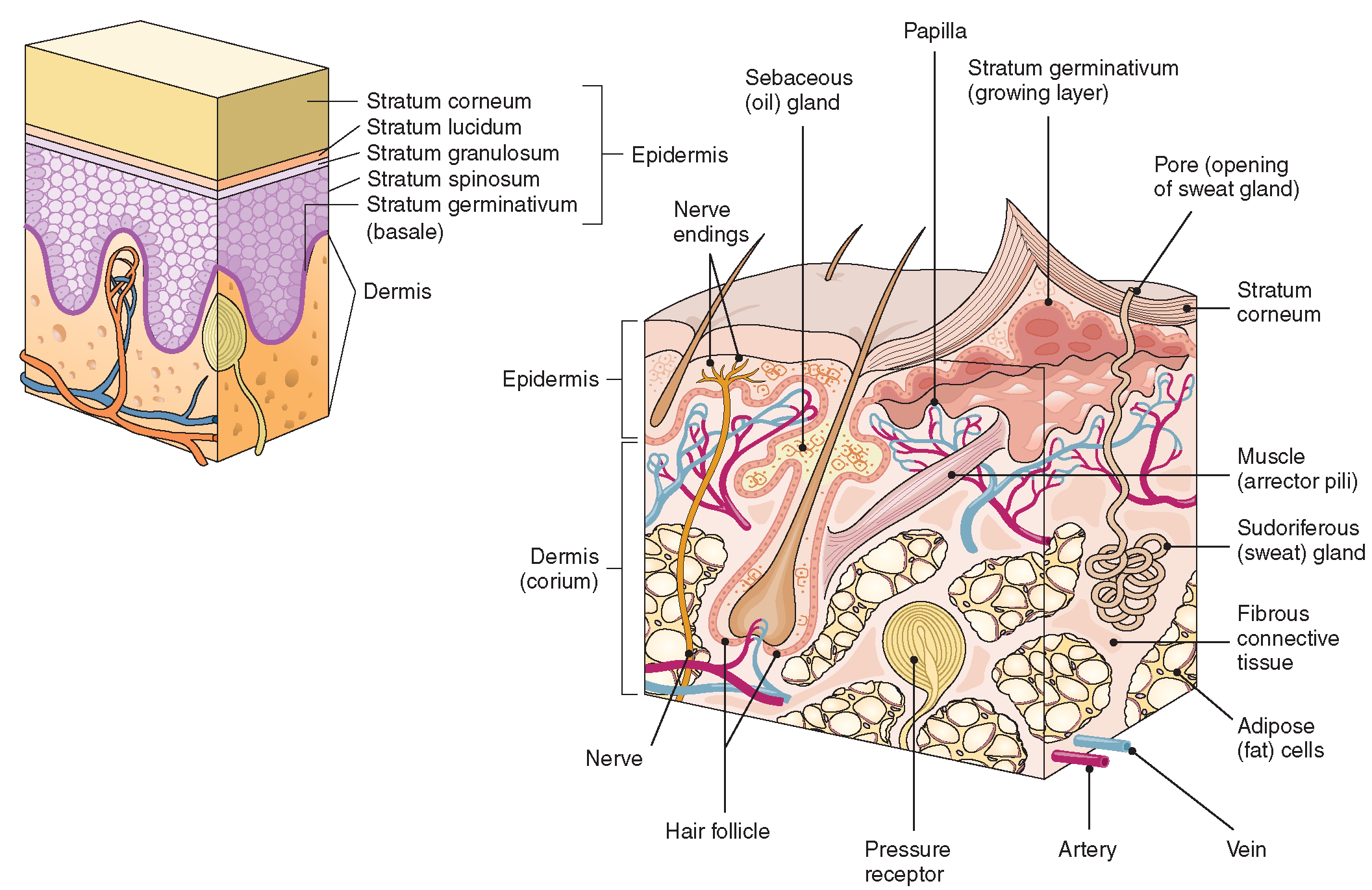
The Integumentary System (Structure and Function) (Nursing) Part 1
Figure 5.1.1 - Layers of Skin: The skin is composed of two main layers: the epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures.

skin structure epidermis, dermis, subcutis (subcutaneous layer or
Figure 5.2 Layers of Skin The skin is composed of two main layers: the epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures.
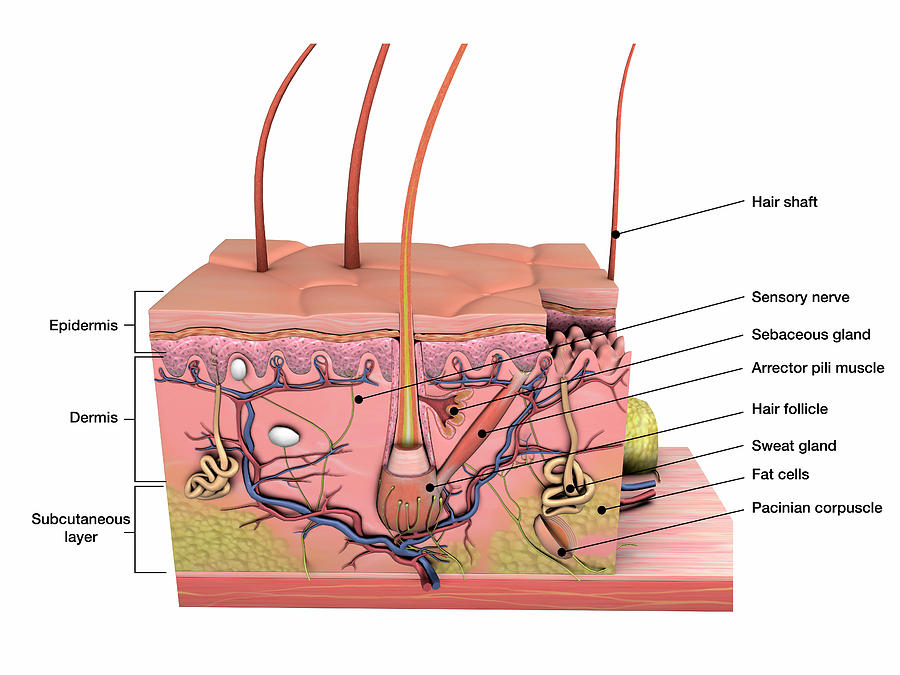
Anatomy Of Human Skin With Labels Photograph by Hank Grebe Pixels
The Layers of the Skin: Interactive Anatomy Model The Layers of the Skin By: Tim Taylor Last Updated: Oct 24, 2017 2D Interactive NEW 3D Rotate and Zoom + Click To View Large Image The skin is by far the largest organ of the human body, weighing about 10 pounds (4.5 kg) and measuring about 20 square feet (2 square meters) in surface area.

Understanding How Your Skin Works School of Natural Skincare
Labeled diagram of the skin. So what's the idea? Spend some time analyzing the skin diagram labeled above. Try to memorize the appearance and location of each structure. Learning the function of each structure will accelerate your ability to memorize, so be sure to check out our detailed article on The Integumentary System parts and functions.

Structure Of Skin Skin Structure and Function LearnFatafat
Diagram of human skin structure Image Add to collection Rights: The University of Waikato Te Whare Wānanga o Waikato Published 1 February 2011 Size: 100 KB Referencing Hub media The epidermis is a tough coating formed from overlapping layers of dead skin cells. Appears in ARTICLE Touch
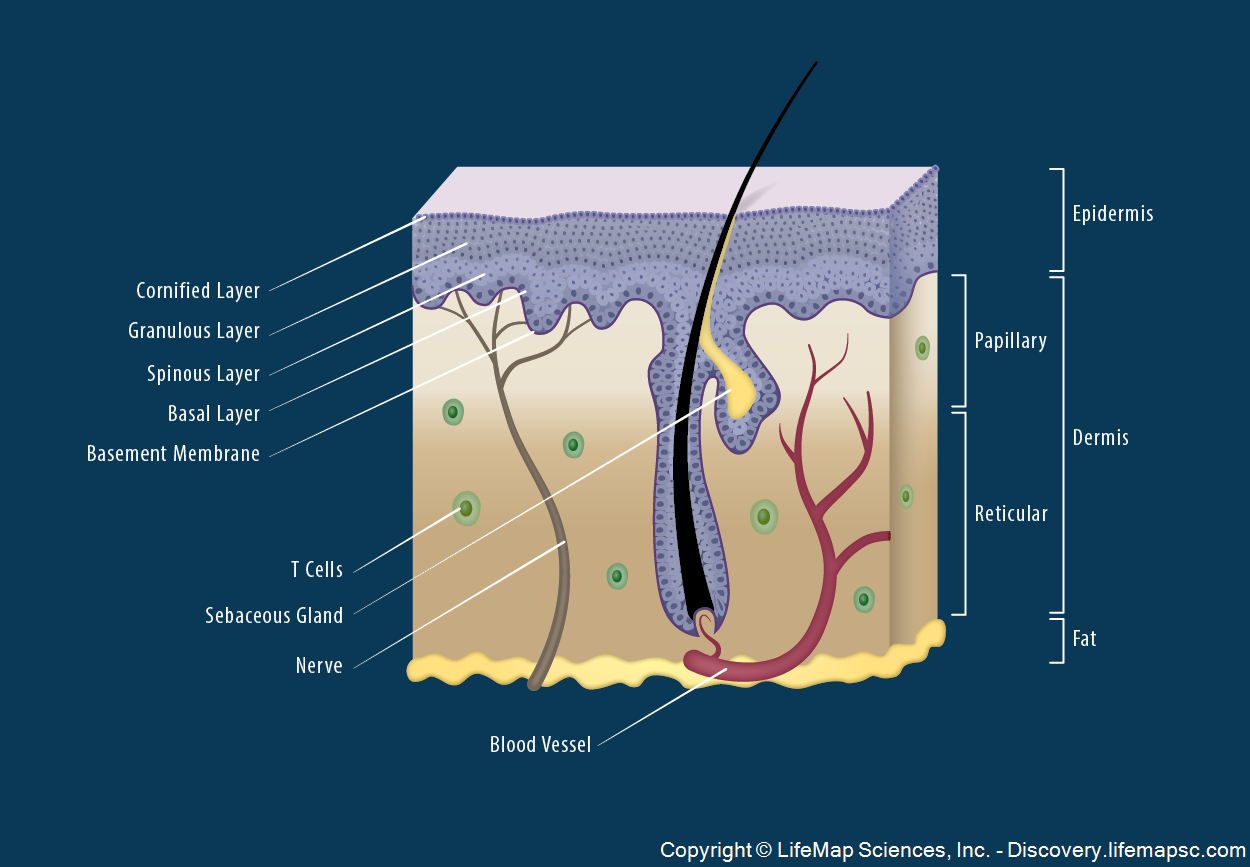
Skin Structure infographic LifeMap Discovery
Undoubtedly, the skin is the largest organ in the human body; literally covering you from head to toe. The organ constitutes almost 8-20% of body mass and has a surface area of approximately 1.6 to 1.8 m2, in an adult. It is comprised of three major layers: epidermis, dermis and hypodermis, which contain certain sublayers.

The skin Understanding cancer Macmillan Cancer Support
Start Quiz Explore Skin Diagram with BYJU'S. Diagram of the skin is illustrated in detail with neat and clear labelling. Also available for free download

Dermis Layers, Papillary Layer, Function Epidermis
The Layers of Your Skin. Your skin includes three layers known as epidermis, dermis, and fat. Some health issues, such as dermatitis and infections, can affect how these different layers work to.
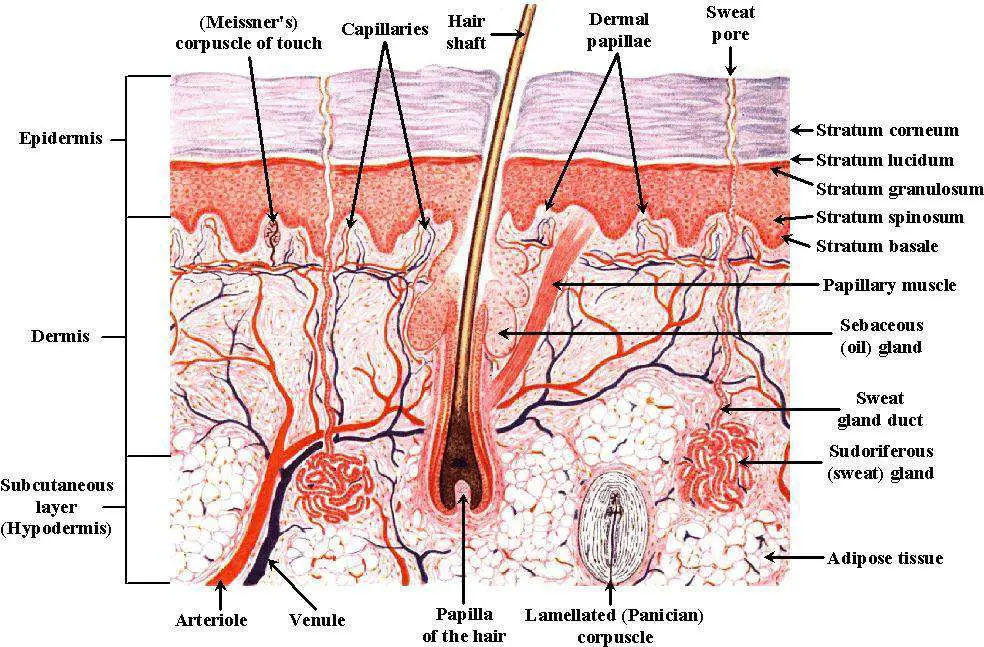
Skin diagram labeled
Description: Layers of the skin. The inner layer of the skin is the dermis, and the outer layer is the epidermis. The epidermis can be specified further in the stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum gransulosum, stratum spinosum and stratum basale. English labels. From 'Human Biology' by D. Wilkin and J. Brainard . Anatomical structures in item:
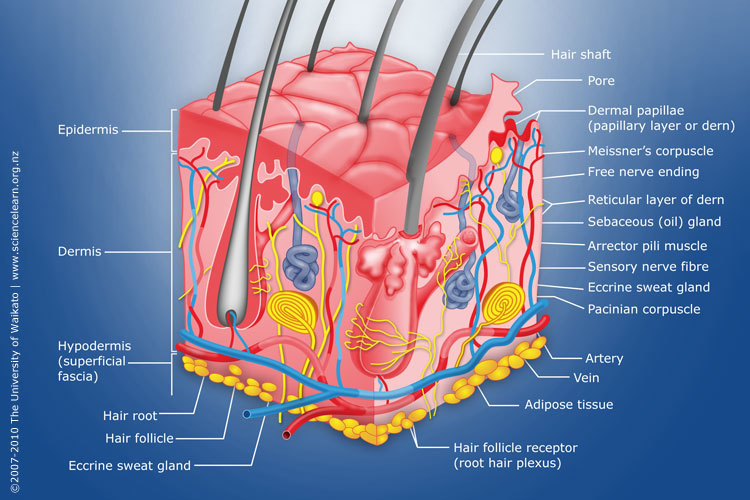
Diagram of human skin structure — Science Learning Hub
1. The outermost layer of the skin is: the dermis / the epidermis / fat layer. 2. Which is the thickest layer: the dermis / the epidermis? 3. Add the following labels to the diagram of the skin shown below: Epidermis, dermis, fat cells, hair shaft, hair follicle, hair erector muscle, sweat gland, pore of sweat gland, sebaceous gland, blood.