
25 Root Structure And Growth Worksheet Answers Worksheet Project List
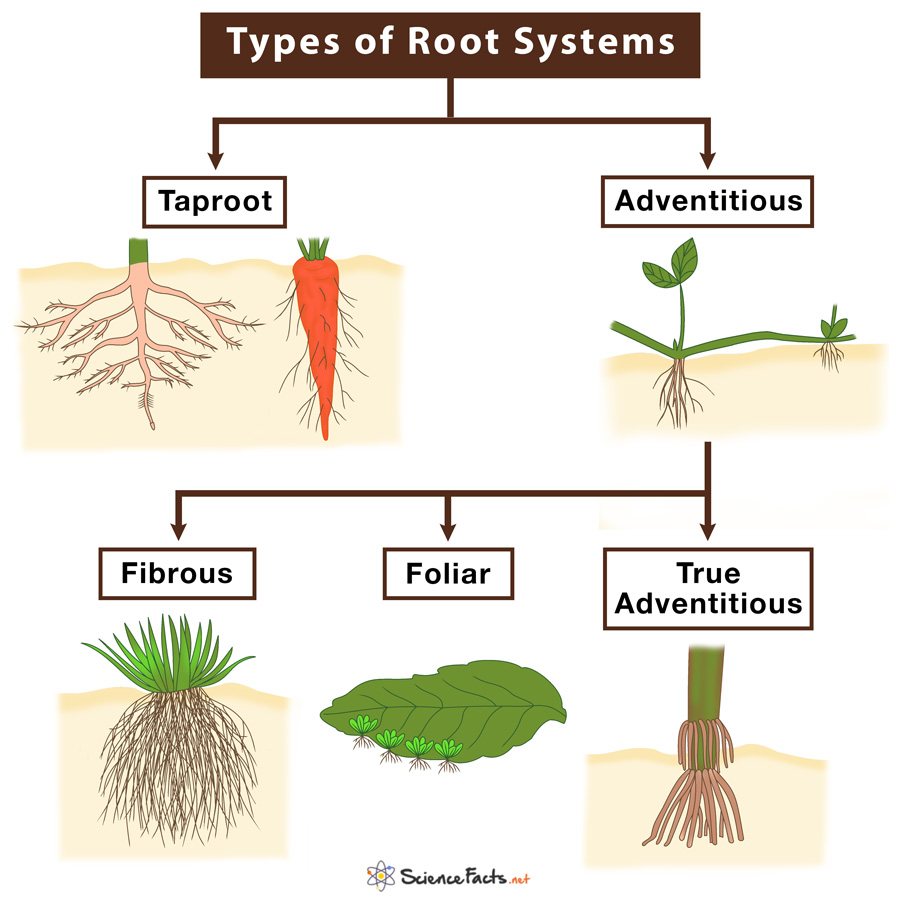
Tap root system Fibrous roots are bushy roots seen mostly in monocotyledons like rice and wheat. Taproots are large central roots from which small lateral roots sprout out. These are primarily seen in dicotyledons like carrots and radish. Adventitious roots originate from branches, stems and leaves.
tree_1 Blog Creative Presentations Ideas
When examining a diagram of the root system, one can observe its hierarchical organization. The primary root, or the first root to emerge from the seed, is the main axis from which all other roots branch. Secondary roots sprout laterally from the primary root, forming a network of roots that reach out in various directions.

Diagram showing internal root structure Royalty Free Vector
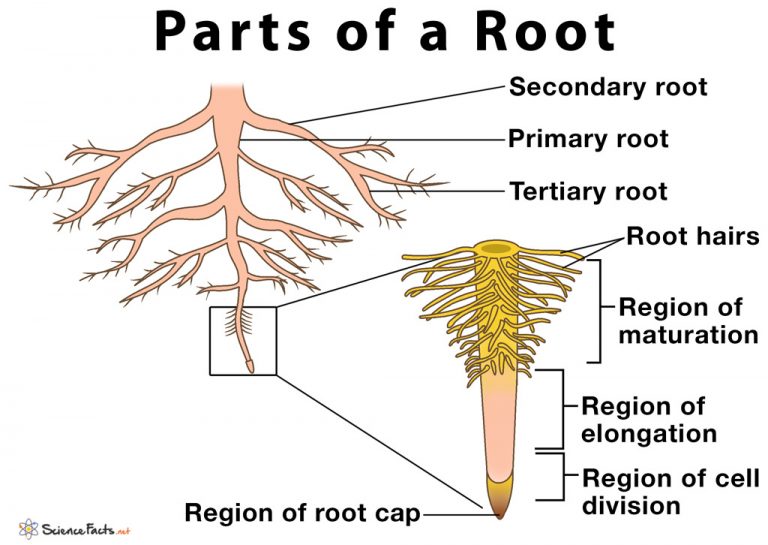
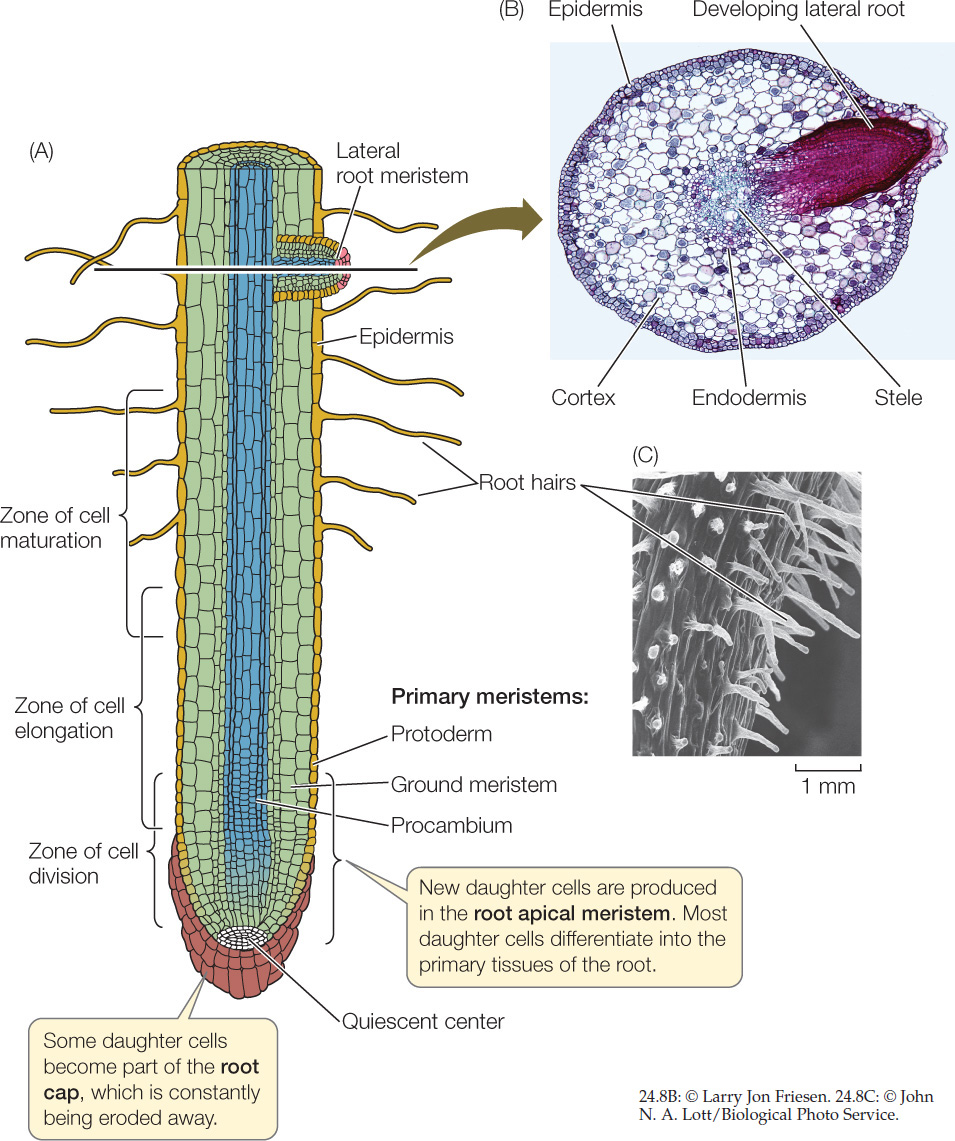
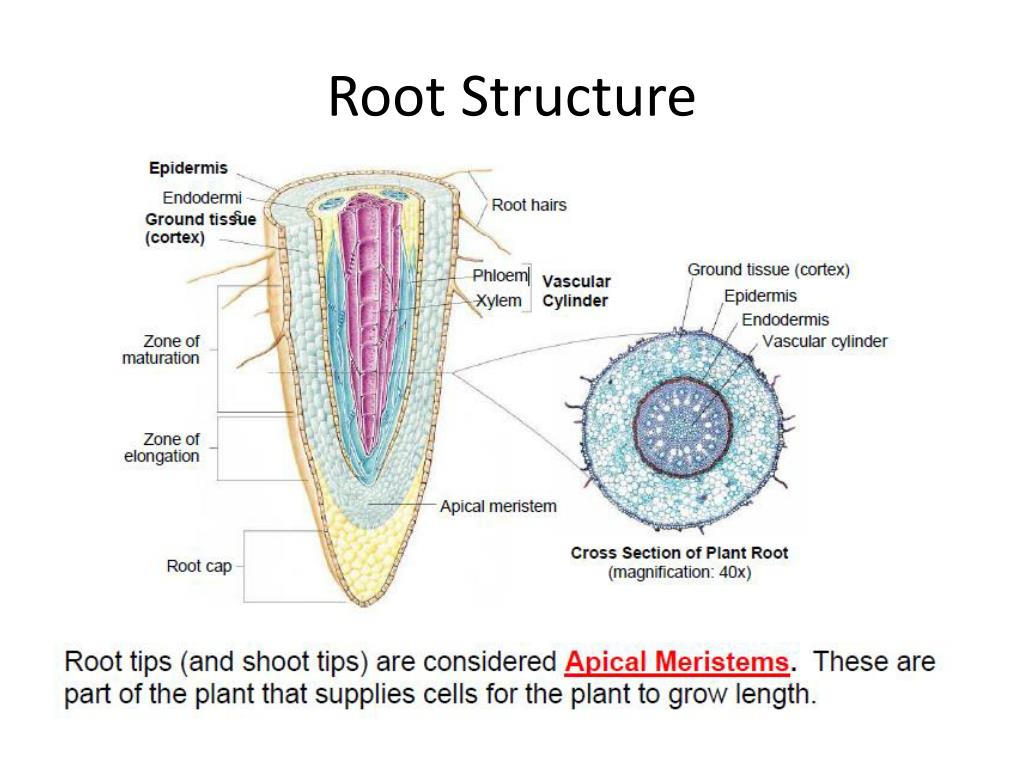
Typical Root: Part # 1. Root Cap: It is a thimble-shaped or cap-like parenchymatous multicellular structure which covers the root meristem. The cells of the root cap secrete mucilage. The latter lubricates the passage of root through the soil. Without it, the tender root would be unable to penetrate the hard soil.
Life Science Page 3 of 34 Science Facts
Root Systems. There are two basic types of root systems in plants: taproot systems and fibrous rootsystems. Both are illustrated in Figure below.. Taproot systems feature a single, thick primary root, called the taproot, with smaller secondary roots growing out from the sides.The taproot may penetrate as many as 60 meters (almost 200 feet) below the ground surface.
Types of Roots With Examples and Diagrams
There are three different types of root structure. A taproot, characteristic of dicots, is a single dominant root from which smaller, secondary roots extend. In a fibrous root system, composed of many small roots, no single root dominates. Taproots stretch deep into the soil, while fibrous roots spread out close to the surface.
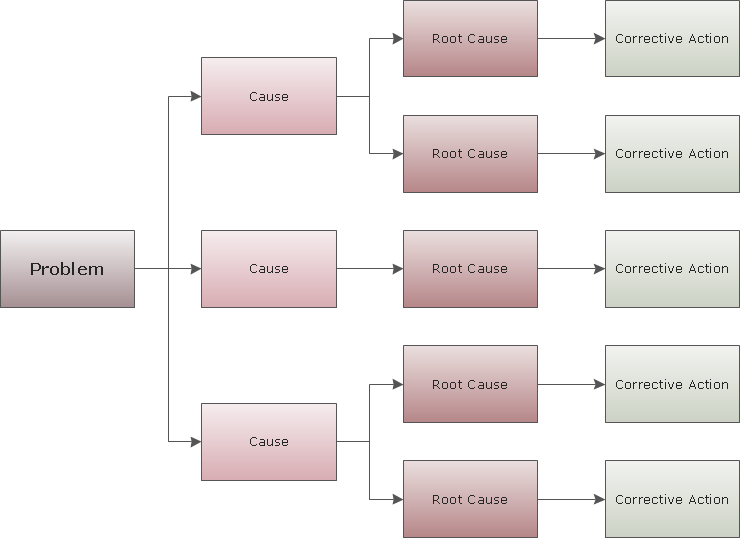
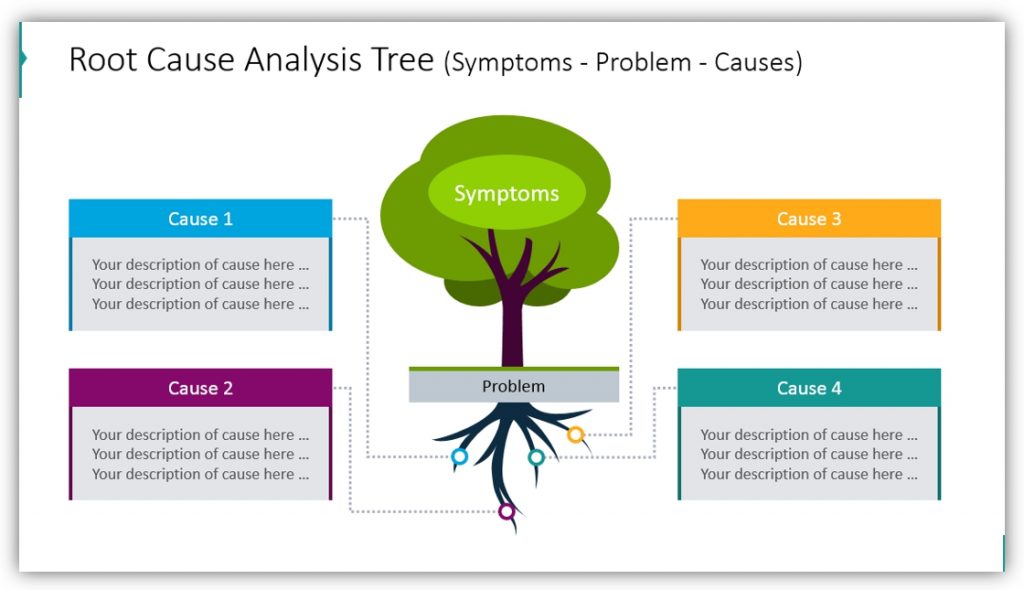
Tree Diagram Root Cause Analysis Template My XXX Hot Girl
The Root: Regions and Functions (With Diagram) Article Shared by ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article, we propose to discuss about the various regions and functions of the root. The root is the descending portion of the plant axis. As opposed to the stem, it is positively geotropic, negatively phototropic and positively hydrotropic.

Parts Of Plants Parts Of Plants For Kids Rabbitsabc
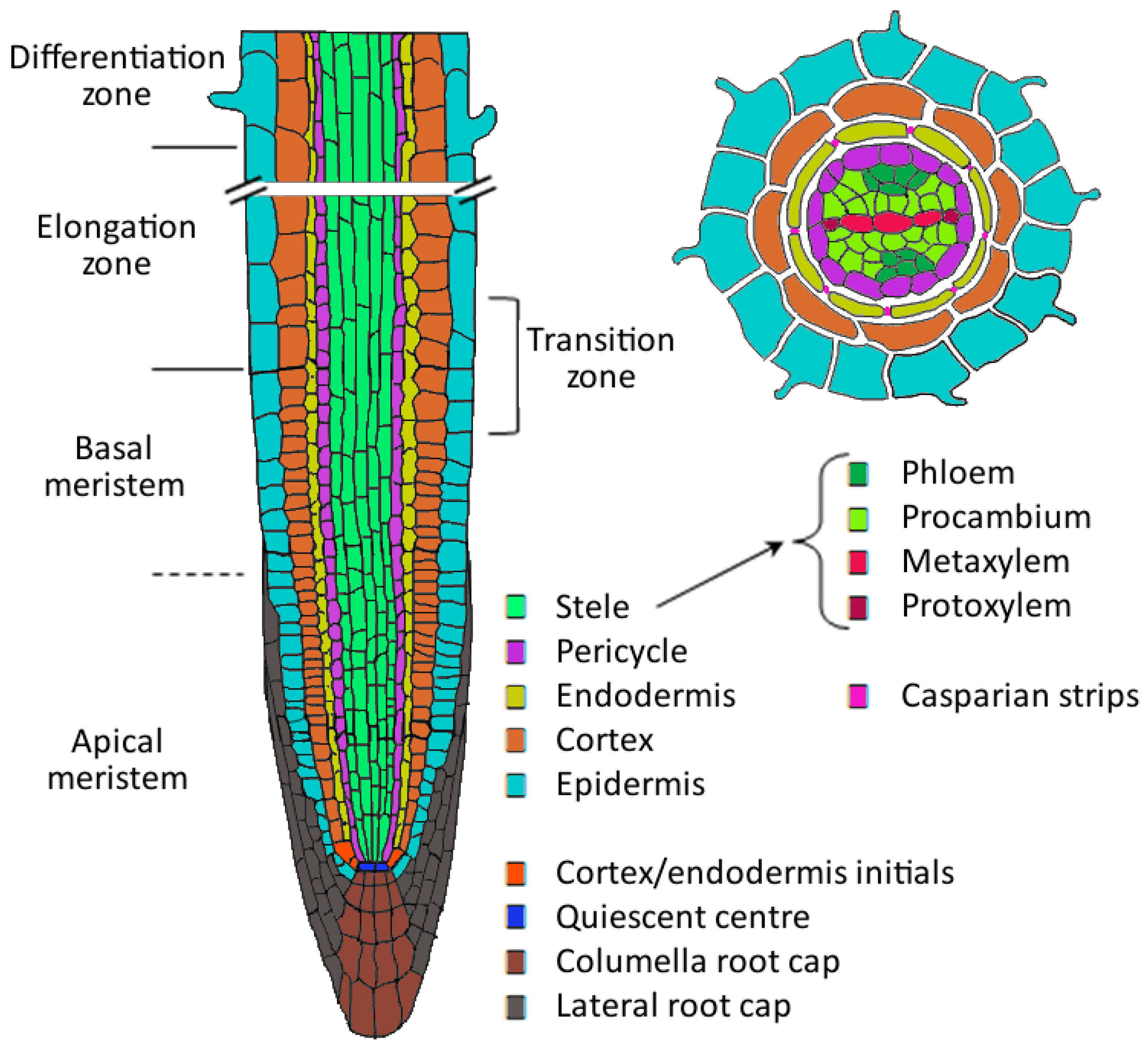
We can see the root cap in the diagram below. Primary Roots. Directly behind the root cap is the root meristem, which is where cell division occurs. This means that when the root grows, the new.
hillis2e_ch24
These include providing structure, supporting the leaves, buds, and flowers. Additionally, the stem will aid in orienting the leaves to maximize photosynthesis. Stems are composed of nodes, points at which leaves and branches attach, and internodes, the regions of stem between the nodes. The petiole is a stalk that anchors each leaf at the node.
Aggregate more than 64 root hair cell diagram super hot in.eteachers
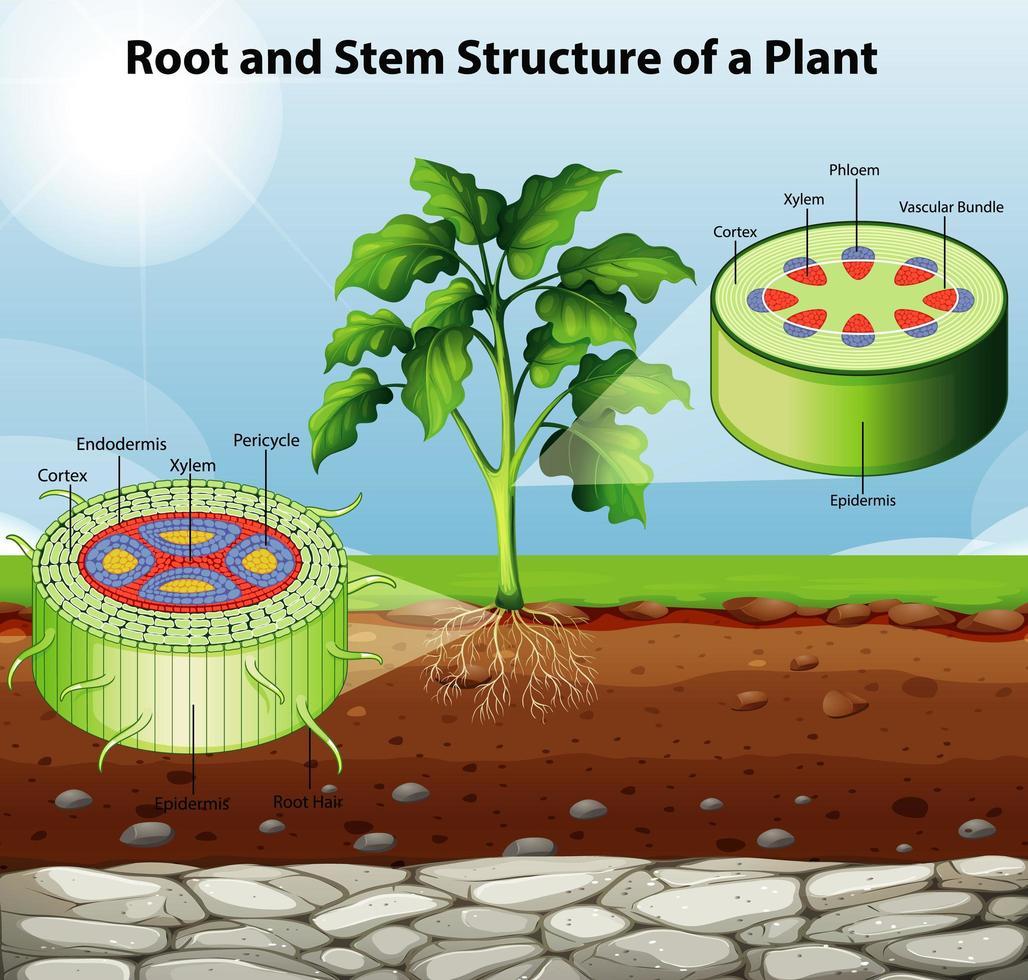
Internal Structure of Root (With Diagrams) Article Shared by ADVERTISEMENTS: The below mentioned article provides an outline of the internal structure of root. The root develops from the radicle of the embryo.
Bare root planting guide Wells Medina Nursery
The root is the descending part of the plant axis, which lies inside the soil. It contains the following parts like Root cap Root Hair Zone of elongation (region of elongation) Zone of maturation (region of maturation) The root typically does not contain chlorophyll, and therefore, it is nongreen.
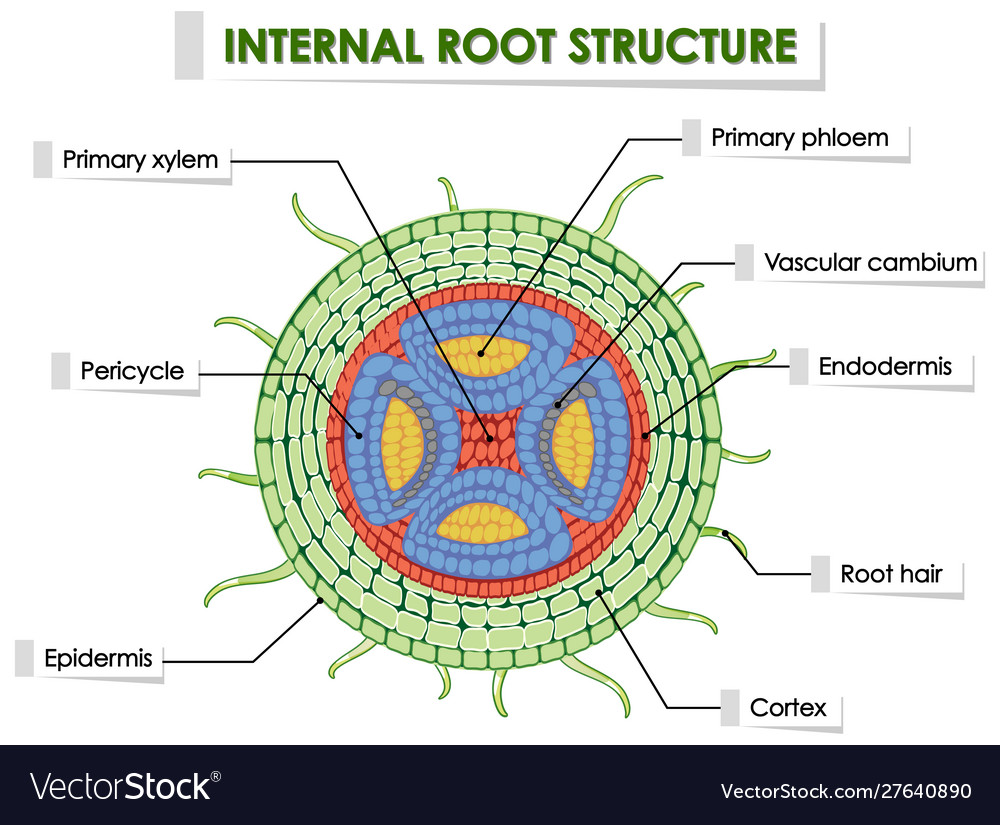
Diagram showing internal root structure Royalty Free Vector
Taproots. Figure 11.3.1 11.3. 1: The carrot vegetable we eat is the taproot of a carrot plant. The large, central root (what we call a carrot) is a taproot and has many much smaller lateral roots that emerge from the sides. These are not root hairs, which would appear more like a microscopic fuzz at the ends of these lateral roots.
PPT Plants Structure and Function PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID776144
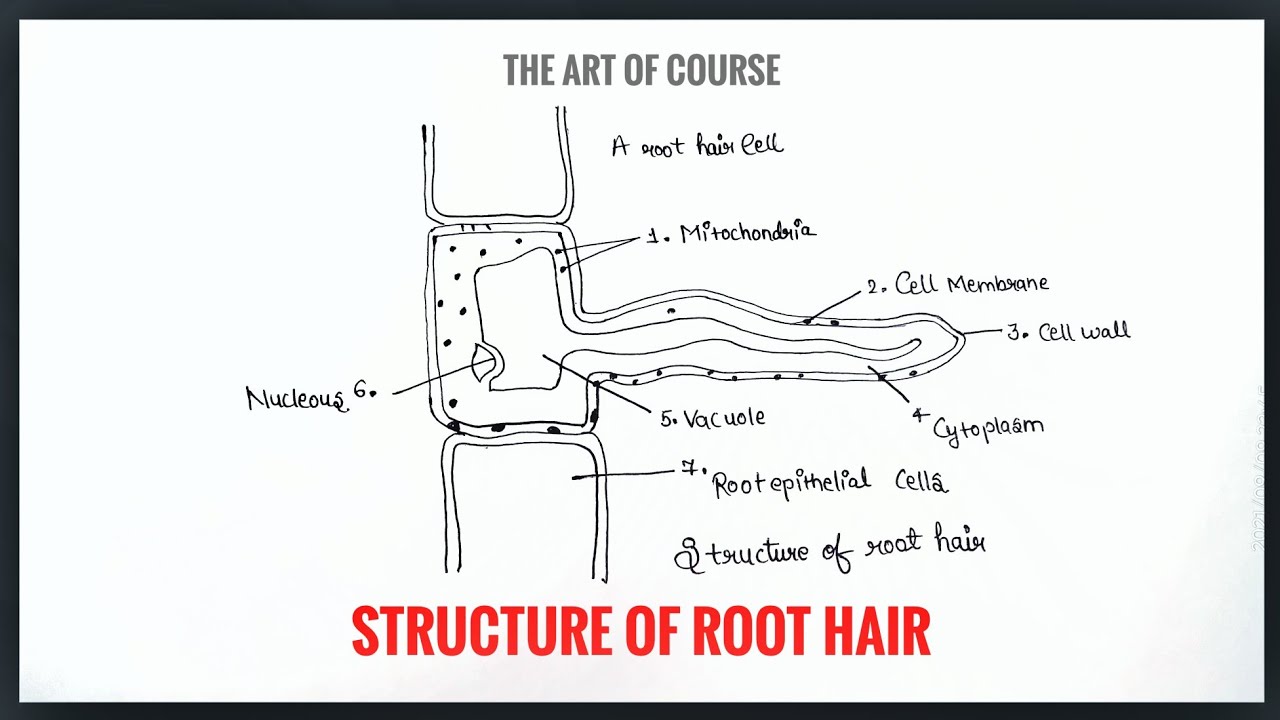
The root structure usually includes a root cap that protects the root as it grows, and root hairs sprout from the main roots epidermis, or outer "skin" layer, which aid in the acquisition of water.
Botany Professor The "root" of the root problem
Monocot roots are fibrous, meaning they form a wide network of thin roots that originate from the stem and stay close to the surface of the soil. In contrast, dicots have "taproots," meaning they form a single thick root that grows deep into the soil and has smaller, lateral branches. 2. Monocot and dicot roots contain multiple tissue.

diagram of root tip KalumKatrian
This area of meristematic activity is called the zone of division. Figure 7.3.1 7.3. 1: Zone of division. As you move up in the root, the cells begin to get larger, developing into primary tissues. This region is called the zone of elongation. Figure 7.3.2 7.3. 2: Zone of elongation.
Plant Root and Stem Diagram 1132892 Vector Art at Vecteezy
3.3 Roots. Though unseen, the roots of a plant also have specialist anatomical features that enable plants to efficiently obtain nutrients and control the substances entering a plant. Figure 3.9. Diagram of the structures of and areas of a developing root. (Image from: Marsland, Douglas. (1964) Principles of modern biology.
IJMS Free FullText Gene Networks Involved in Hormonal Control of Root Development in
ROOT ANATOMY: DICOT ROOT CROSS SECTION Dicot Root Diagram Reveals Internal Structure of Dicot Root. A thin transverse section of the young dicot root of Gram, Sunflower or Pea reveals the following structures under the microscope: 1. Epiblema or Piliferous Layer. This is the outermost layer of root-derived from the protoderm of the apical meristem.