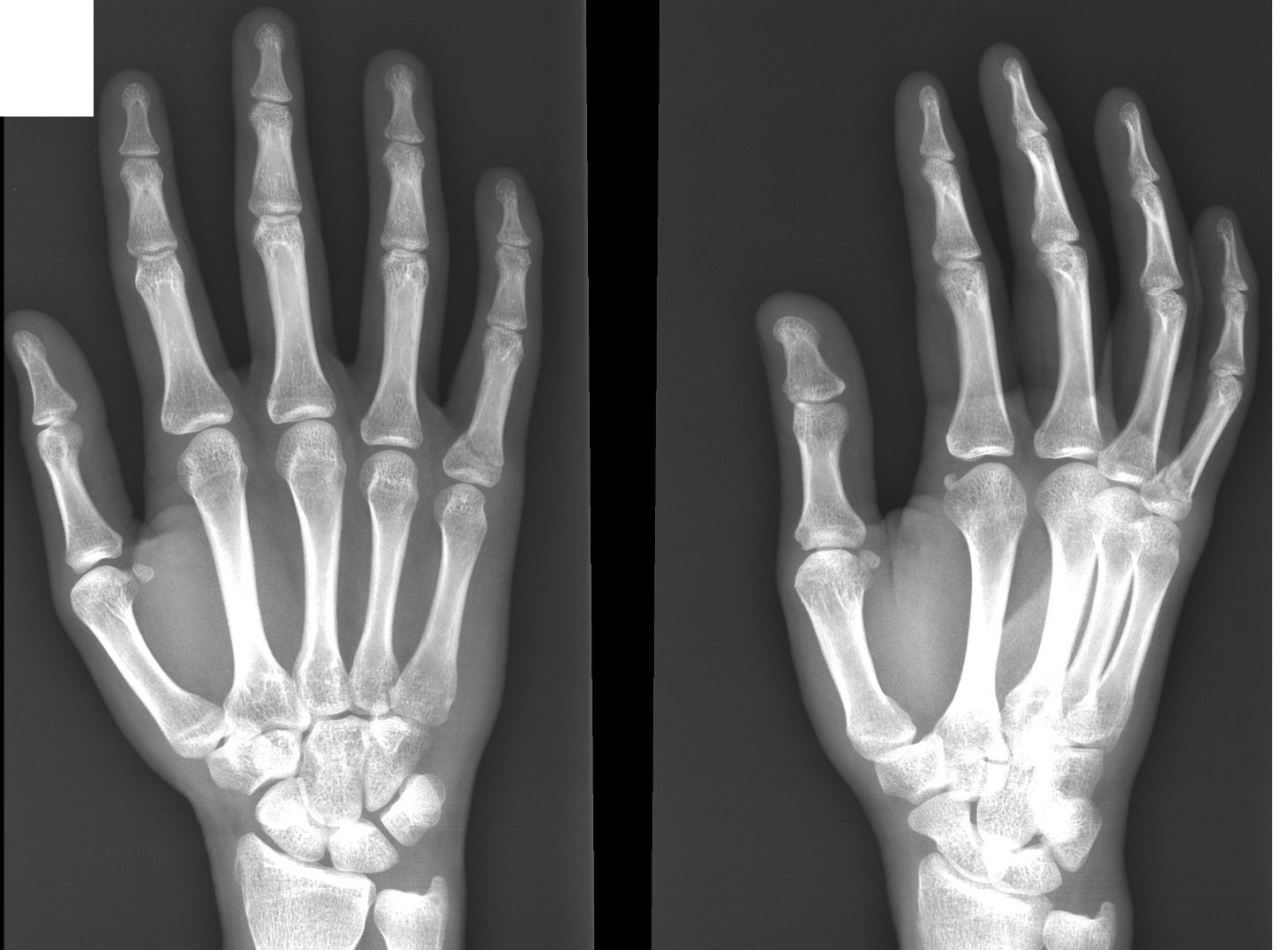
Imaging Case of the Week 45 Emergucate
Wrist x-ray with labeled osseous anatomy. An official website of the United States government. Here's how you know.. [J Hand Surg Am. 2009] In vivo length changes of selected carpal ligaments during wrist radioulnar deviation. Xu J, Tang JB. J Hand Surg Am. 2009 Mar; 34(3):401-8.
Hand xray
visualizes the waist of scaphoid but is limited by overlap of carpal bones. scaphoid view. 30° wrist extension, 20° ulnar deviation. IR oblique. best view to see the waist and distal pole of scaphoid. if radiographs are negative and there is a high clinical suspicion, repeat radiographs in 14-21 days. Optional views.

Normal Hand X Ray Colorvir Xray photo of normal right hand Stock Image Find the
Zoe Little, specialty trainee 3 in trauma and orthopaedics, ; John Murphy, consultant orthopaedic surgeon; 1 Department of Trauma and Orthopaedics, Northwick Park Hospital, Harrow HA1 3UJ, UK; Correspondence to: zoe.little{at}doctors.org.uk
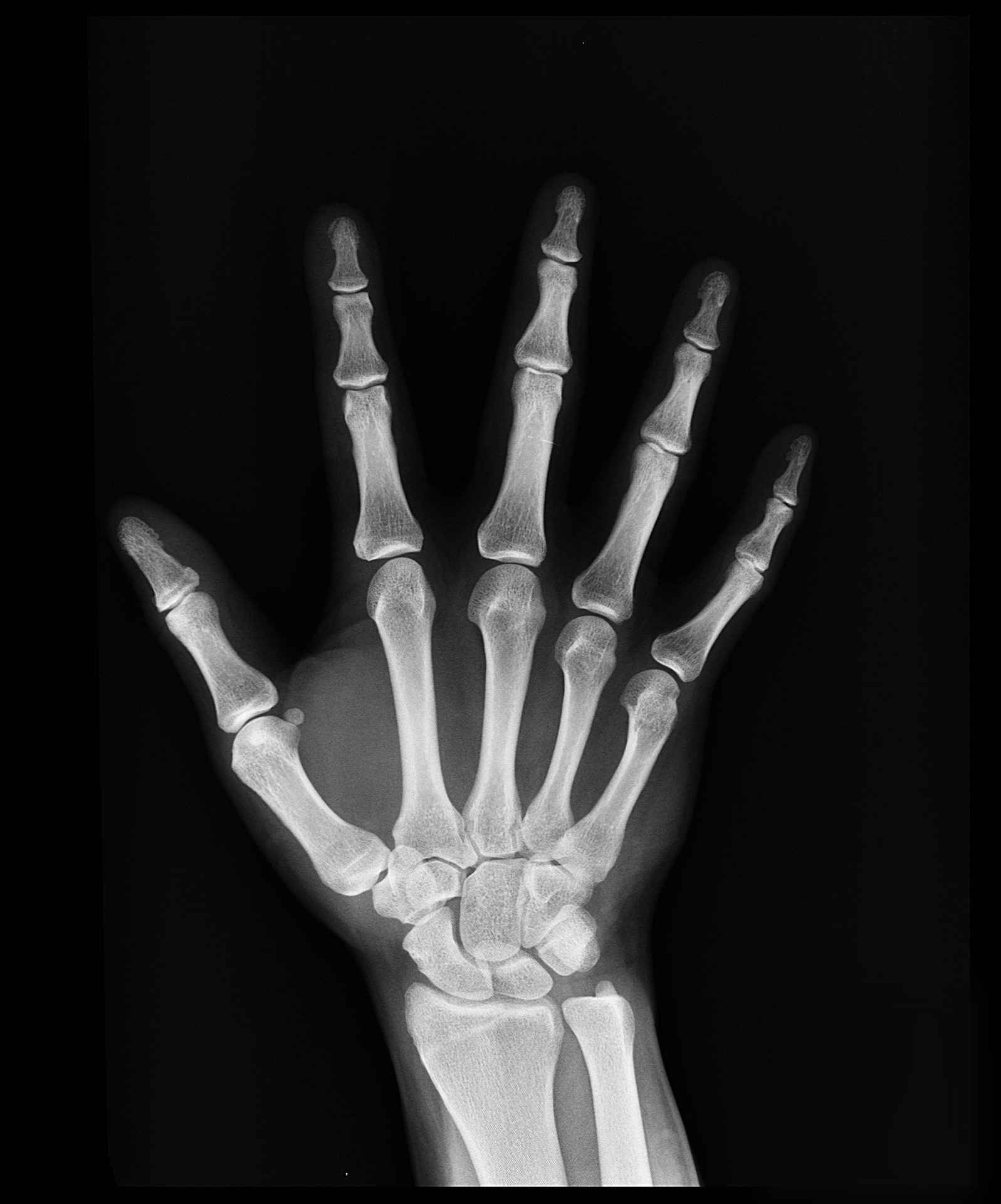
Hand XRay
Diagnostic Labels for Musculoskeletal Pain. Appropriate diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain involves a multifactorial approach that includes the history of the disease, a thorough physical.

Hand xray. Causes, symptoms, treatment Hand xray
Key points. Finger injuries visible on X-ray include bone fractures, dislocations and avulsions. The hand comprises the metacarpal and phalangeal bones. Fractures and dislocations are usually straightforward to identify, so long as the potentially injured bone is fully visible in 2 planes. Finger joints commonly dislocate and are susceptible to.
What a normal hand xray looks like (left) and what I managed to do to my hand(right). Local
Labels: Base of fifth metacarpal Base of middle phalanx of middle finger Base of proximal phalanx of ring finger Capitate Distal phalanx of index finger Distal phalanx of thumb Hamate Head of fifth metacarpal Head of middle phalanx of middle finger Head of ulna Head of proximal phalanx of ring finger Hook of hamate Lunate Pisiform

Hand Radiographic Anatomy wikiRadiography Radiology, Radiology student, Medical anatomy
A hand X-ray (radiograph) is a test that creates a picture of the inside of your hand. The picture shows the inner structure ( anatomy) of your hand in black and white. Calcium in your bones absorbs more radiation, so your bones appear white on the X-ray.

Radiology Schools, Radiology Student, Radiology Technician, Radiology Imaging, Medical Imaging
This guide provides a step-by-step approach to interpreting wrist X-rays and includes examples of the key pathology you may come across. Anatomy The intricate anatomy of the wrist makes wrist X-ray interpretation a challenging task.

Read on to find out more about my review areas on a hand XRay... 👨🏽💻Hand xrays are
Hand X-Ray Anatomy and Interpretation Checklist 1. Soft tissues - Look carefully at the soft tissue over all the bones for any swelling or foreign body. The swelling should prompt a careful search of the underlying bone or joint.⠀ 2. Bones - All the bones of the hand should be examined carefully and systematically.

Xray image showing the left hand wrist in dorsal view. The carpal... Download Scientific Diagram
A recommended systematic checklist for reviewing musculoskeletal exams is: soft tissue areas, cortical margins, trabecular patterns, bony alignment, joint congruency, and review areas. Review the entire radiograph, regardless of perceived difficulty.

Hand Radiographic Anatomy wikiRadiography Diagnostic imaging, Medical knowledge, Medical anatomy
The locations of the epiphyses of the phalanges and metacarpals and the radiographic characteristics of the nutrient artery canals are key practical aspects of the radiographic anatomy of the hand. The phalangeal and metacarpal epiphyses are differently located, and even among the metacarpals, the location of the growth centers is not uniform.

Hand X Ray Medical Art Library
Summary indications suspicion of bony injury assessment of radiopaque foreign body assessment of joint disease procedure AP and oblique views of the hand a lateral view is of little use unless answering specific questions extends from the radiocarpal joint to the tips of fingers similar series wrist series

Wrist Radiographic Anatomy wikiRadiography Radiology student, Medical radiography, Medical
Hand x-rays are indicated for a variety of settings, including: trauma with suspected fracture suspected metacarpal dislocation foreign body detection and localization investigation of joint pain and/or deformity rheumatoid arthritis osteoarthrosis Projections Standard projections PA view
Related Keywords & Suggestions for hand x ray anatomy
Hand Bone X-Ray (Radiography) uses small amounts of electromagnetic radiation for imaging of bones in the hand and wrist. Bone X-Rays are painless, quick and simple ways of viewing bone and joint abnormalities for assessment, diagnosis and treatment purposes. Hand X Ray: Definition

5 ways to use Section Options
Hand (oblique view) | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org Hand (oblique view) Last revised by Andrew Murphy on 23 Mar 2023 Edit article Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data The hand oblique view is part of a two view series metacarpals, phalanges, carpal bones and distal radial ulnar joint. Indications

[Figure, Wrist xray with labeled osseous anatomy. Contributed by John Copeland, DO
The standard examination of the hand generally consists of a posterior-anterior (PA) image and a PA oblique image (3/4 image). For a PA image, the hand lies flat on the x-ray plate, at the level of the shoulder with the elbow in 90 degrees flexion. The x-ray beam will pass through the hand from dorsal to palmar (fig. 2).