
Positive Energy Flow, Plants & Stress Relief HubPages
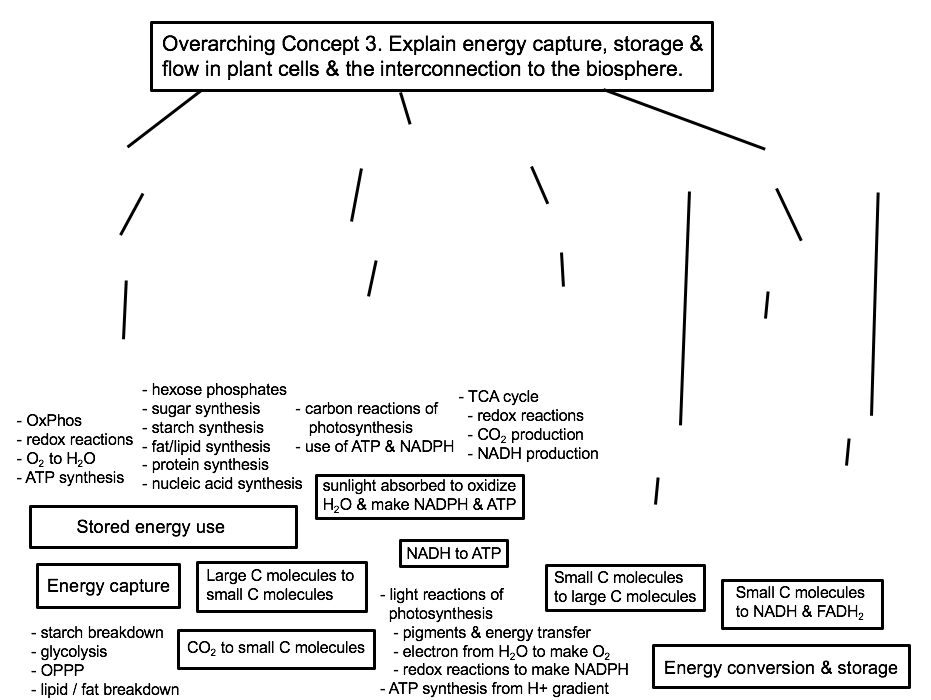
4.5 Energy and Metabolism. Scientists use the term bioenergetics to discuss the concept of energy flow ( Figure 1) through living systems, such as cells. Cellular processes such as the building and breaking down of complex molecules occur through stepwise chemical reactions. Some of these chemical reactions are spontaneous and release energy.

Concept Map Of Energy Flow In An Ecosystem United States Map
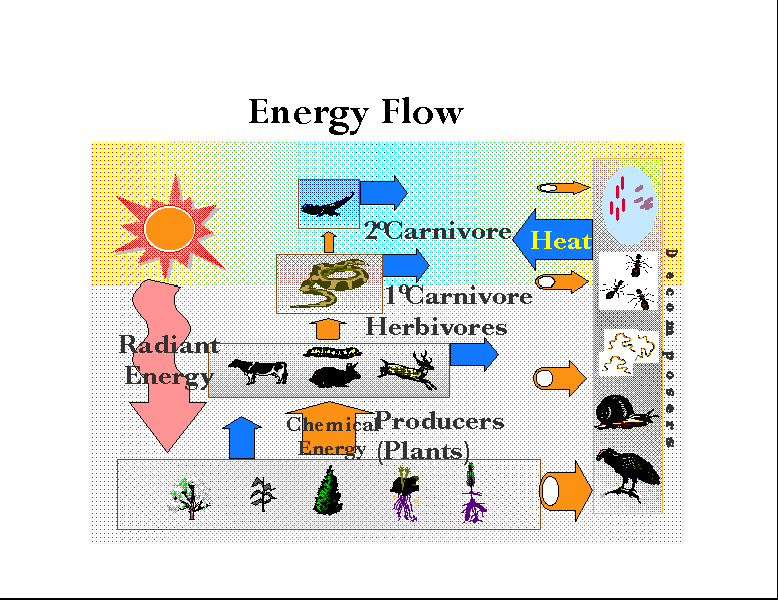
Energy flow (ecology) A food pyramid and a corresponding food web, demonstrating some of the simpler patterns in a food web. A graphic representation of energy transfer between trophic layers in an ecosystem. Energy flow is the flow of energy through living things within an ecosystem. [1] All living organisms can be organized into producers and.
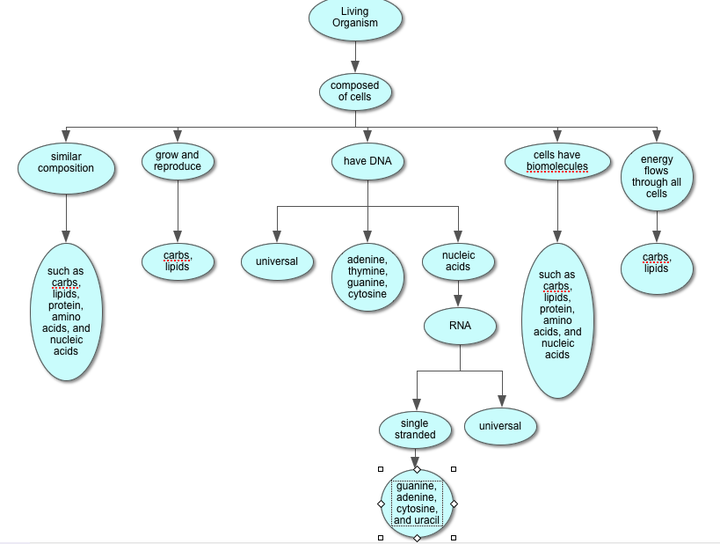
Energy Flow In Plants Concept Map Maping Resources
Primary producers—usually plants and other photosynthesizers—are the gateway for energy to enter food webs. Productivity is the rate at which energy is added to the bodies of a group of organisms—such as primary producers—in the form of biomass. Gross productivity is the overall rate of energy capture. Net productivity is lower.

12+ energy flow in plants concept map NeelamNaoise
This allows chemoautotrophs to synthesize complex organic molecules, such as glucose, for their own energy and in turn supplies energy to the rest of the ecosystem. Figure 56.2.1 56.2. 1: Swimming shrimp, a few squat lobsters, and hundreds of vent mussels are seen at a hydrothermal vent at the bottom of the ocean.
Teaching biology Energy Flow
After the plant uses the energy from glucose for its own needs, the excess energy is available to the organism that eats the plant. The herbivore uses the energy from the plant to power its own life processes and to build more body tissues. However, only about 10% of the total energy from the plant gets stored in the herbivore's body as extra.
ENERGY FLOW IN ECOSYSTEM
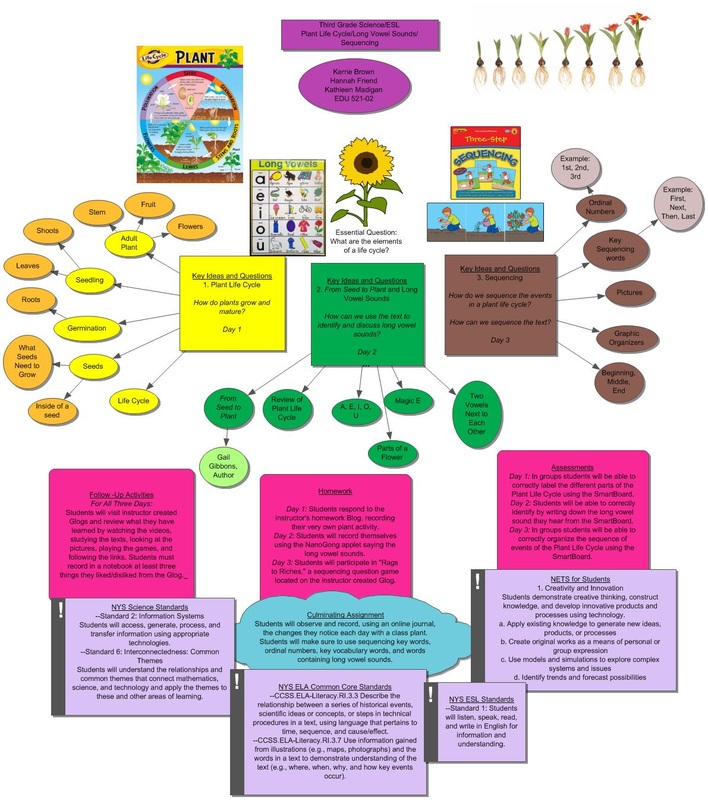
energy flow in plants: concept map Click the card to flip 👆 a) sunlight provides energy for --> b) photosynthesis (occurs in chloroplasts) --> produces oxygen and sugar --> inputs for cellular respiration (occurs in mitochondria) --> produces ATP and carbon dioxide --> provide carbon for photosynthesis Click the card to flip 👆 1 / 22 Flashcards

Energy Flow In Plants Concept Map Maping Resources
Figure 20.1.1 20.1. 1: A (a) tidal pool ecosystem in Matinicus Island, Maine, is a small ecosystem, while the (b) Amazon rainforest in Brazil is a large ecosystem. (credit a: modification of work by Jim Kuhn; credit b: modification of work by Ivan Mlinaric) There are three broad categories of ecosystems based on their general environment.
Energy Flow In Plants Concept Map Maps Database Source The Best Porn
Energy Flow in Plants -- Concept Map Part A - Photosynthesis and respiration in plants Drag the labels from the left to their correct locations in the concept map on the right. Not all labels will be used. a. sunlight b. photosynthesis c. chloroplasts d. sugar e. chlorophyll f. carbon dioxide g. cellular respiration h. mitochondria.

Energy Flow In Plants Concept Map
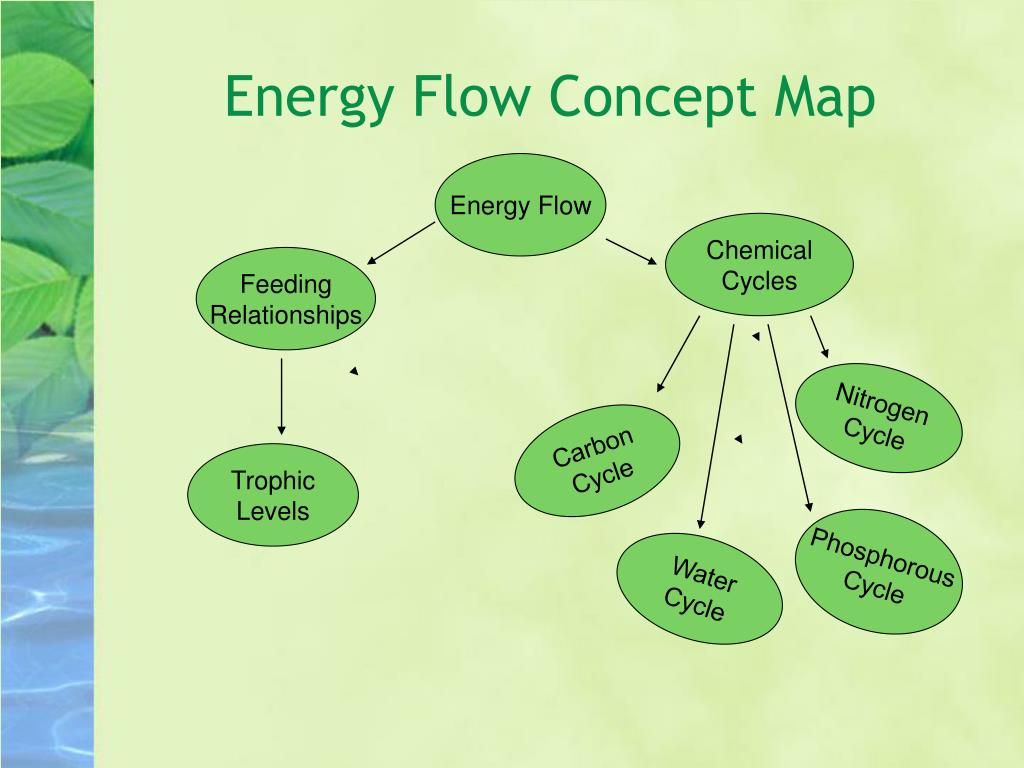
Flow of Energy in Ecosystems Mind Map ( Concept Map ) | Earth Science | CK-12 Foundation Flow of Energy in Ecosystems Reveals that energy is transferred between organisms in one direction in a food chain, but that interconnected food chains make a food web. Estimated3 minsto complete Progress Practice Flow of Energy in Ecosystems Practice
Teaching Technology Plants Concept Map
Energy loss by respiration also progressively increases from lower to higher trophic states (Fig. 3.15). In the energy flow process, two things become obvious. Firstly there is one way along which energy moves i.e. unidirectional flow of energy. Energy comes in the ecosystem from outside source i.e. sun.

Energy Flow In Plants Concept Map World Map
Energy Flow in Plants - Concept Map < 11 of 1 down to fuel cellular work is this actives you will complete concept map showing the mediese geprion und garden plat Part A - Photosynthesis and respiration in plants Drag the labels from the left to their correct locations in the concept map on the right Notbeles will be used View Available Hits) Re.
Energy Flow In Plants Concept Map Ideas of Europedias
Social Studies. World Languages. Through the process of photosynthesis, plants harness the Sun's energy and in so doing make many forms of life—including human life—possible. What path does this energy follow, and how is it transferred from one type of organism to another? In this feature from NOVA: Earth, learn why 400 pounds of corn.
Energy Flow In Plants Concept Map Maping Resources
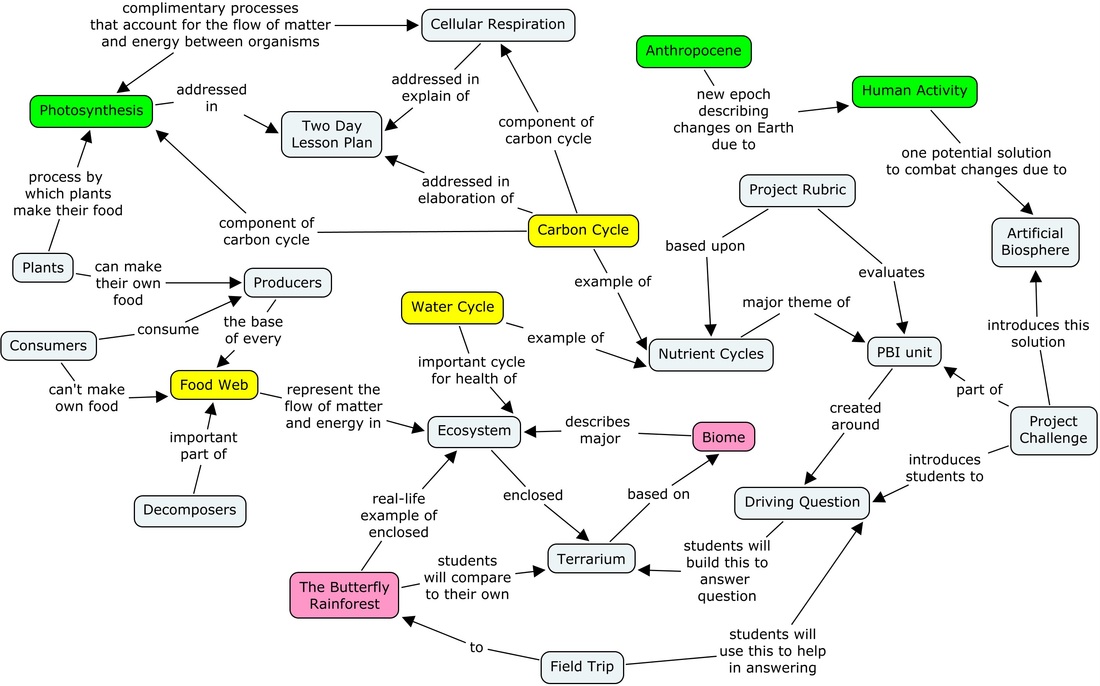
A photosynthesis concept map is a learning tool that lets students more easily and concretely understand the steps of photosynthesis by using a clear visual aid.. during stage four—the Calvin Cycle—the plant converts carbon dioxide and the energy carrier ATP into glucose sugar. Finally, in step five, they store the glucose as energy and.
Energy Flow In Plants Concept Map Ideas of Europedias
This page titled 5.2.7: Energy and Energy Flow is shared under a CC BY-NC 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Melissa Ha, Maria Morrow, & Kammy Algiers ( ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative) . Energy flows through a community as a result of trophic interactions. Energy is defined as the ability to do work, or to.

12+ energy flow in plants concept map NeelamNaoise
Key points: Primary producers (usually plants and other photosynthesizers) are the gateway for energy to enter food webs. Productivity is the rate at which energy is added to the bodies of a group of organisms (such as primary producers) in the form of biomass. Gross productivity is the overall rate of energy capture.
Energy Flow In Plants Concept Map Maps For You
The definition of energy flow is the transfer of energy from the sun and up each subsequent level of the food chain in an environment. Each level of energy flow on the food chain in an ecosystem is designated by a trophic level, which refers to the position a certain organism or group of organisms occupies on the food chain.